Managing Application File Permissions
Learn how to update and reset file permissions for your KloudBean application. This guide covers the two types of file ownership options and how to properly configure permissions to ensure your application files are accessible and secure.
Overview
File permissions mean the permissions set on the web files which are present in your root directory. It is important to update permissions, as sometimes when you add files to your root folder, due to lack of web permissions, files are not accessible and you may face "permission denied" errors. KloudBean provides a very easy way to reset your file permissions.
Why File Permissions Matter
Proper file permissions are essential for:
- File Accessibility: Ensures web files are accessible by the web server and users
- Security: Prevents unauthorized access to sensitive files
- Application Functionality: Allows applications to read, write, and execute files as needed
- Developer Access: Enables developers to work with files through SSH/SFTP access
- Preventing Errors: Avoids "permission denied" errors that can break your application
Understanding KloudBean File Ownership Types
KloudBean provides two types of file ownership options:
1. Admin User (Server Master User)
- Prefix:
admin_(e.g.,admin_user) - Privileges: Maximum privileges - this user has full access to server resources
- Use Case: When you need maximum control and access to application files
- Access Level: Can access and modify files across the server
2. App System User (Application-Specific User)
- Type: Application-specific user
- Privileges: Has permissions to that particular app only
- Use Case: When you want to restrict access to a specific application
- Access Level: Limited to the specific application directory only
Group Ownership
- Group:
www-data - Purpose: This is the web server group that needs access to serve files
- Consistent: Group ownership is kept as
www-datafor both ownership types
Prerequisites
Before updating file permissions, ensure you have:
- An Active KloudBean Application: Your application must be created and running
- SSH Access (Optional): SSH access is helpful for verifying permissions, though not required
- Understanding of Ownership Types: Basic understanding of admin user vs. app system user
Updating Application File Permissions
Step 1: Navigate to File Permissions Section
To update your application file permissions:
- Navigate to Application Administration: Log in to your KloudBean dashboard and open the application administration page for your desired application.
- Access App Settings: Go to the "App Settings" tab in the application settings menu.
- Open General Settings: Navigate to the "General" section within App Settings.
- Locate Permissions Option: On this page, you will see an option "Reset Application Files Permissions".
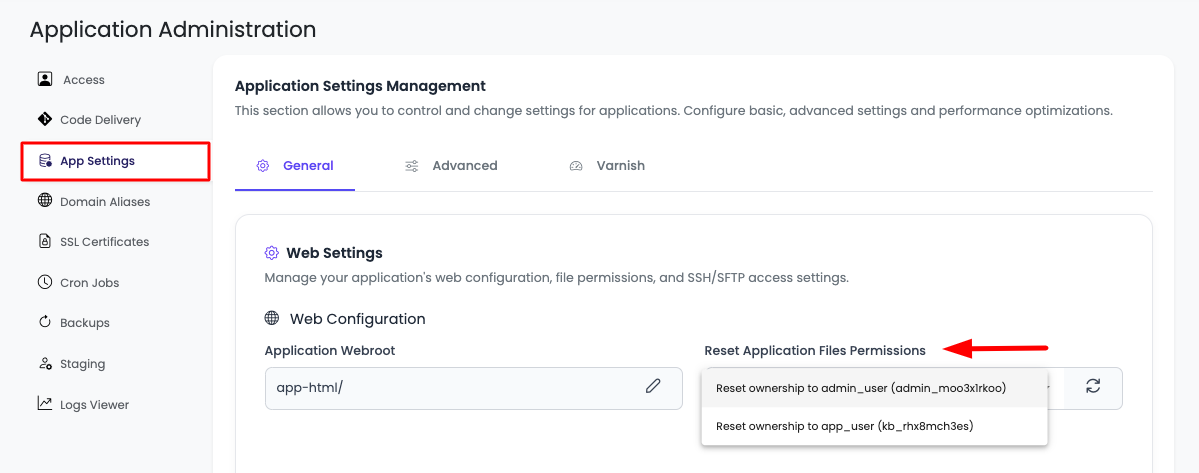
Step 2: Select Ownership Type
In the dropdown, you will see both options:
- Reset Permission to Admin User: Sets ownership to the server master user
- Reset Permission to App System User: Sets ownership to the application-specific user
Important Considerations:
- Admin User Selection: If you select admin user, you'll have maximum privileges on these files, but developers accessing through app user will have less privileges
- App System User Selection: If you want to give permissions to app user, then make sure you set permissions accordingly so that developers who are accessing the app through app user have sufficient rights on these files
- Developer Access: Consider who needs access to the files when choosing the ownership type
Step 3: Reset Permissions to Admin User
To set permissions to admin user:
- Select Admin User: Choose "Reset Permission to Admin User" from the dropdown.
- Click Reset Permissions: Click on the "Reset Permissions" button.
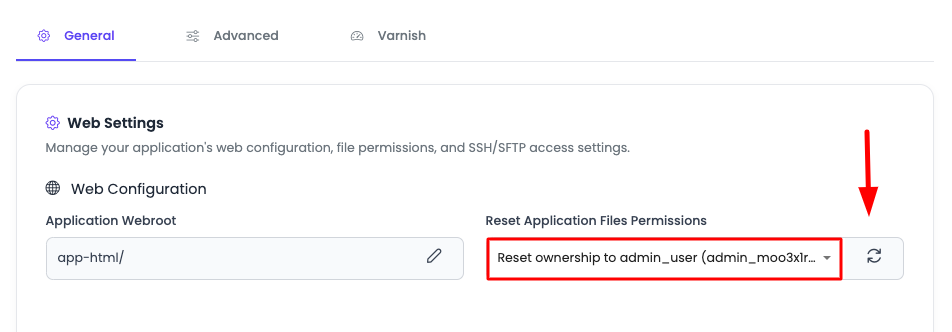
- Wait for Update: Your permissions will be updated and assigned ownership to admin user.
- Verification: The system will confirm when permissions have been reset.
Step 4: Verify Permissions (Admin User)
To validate permissions, you can SSH into the server and check the current ownership of files:
-
SSH into Server: Connect to your server using SSH with admin credentials.
-
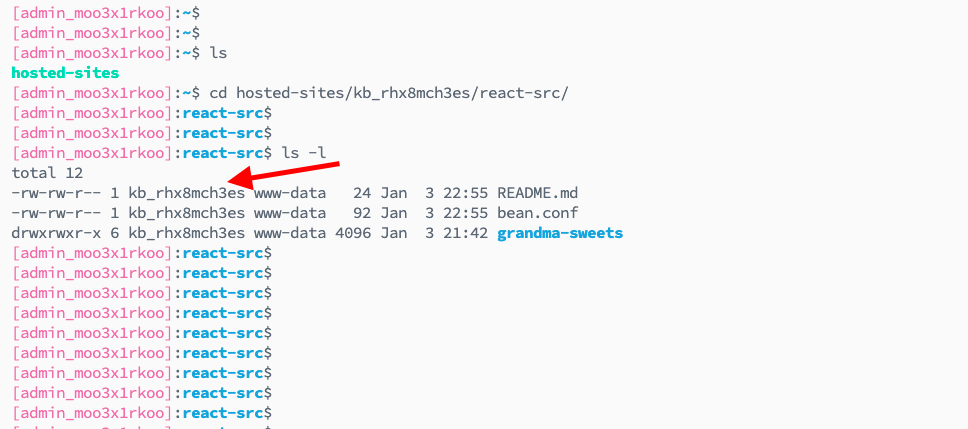
Navigate to Application Directory: Change directory to your application's source directory:
cd /home/admin/hosted-sites/<app_system_user>/<app_type>-srcnoteReplace
<app_system_user>with your actual app system user and<app_type>with your application type (e.g.,react-src,flask-src,djnago-src). -
Check Permissions: Run the command:
ls -l -
View Current Permissions: You will see the current permissions and ownership of files.
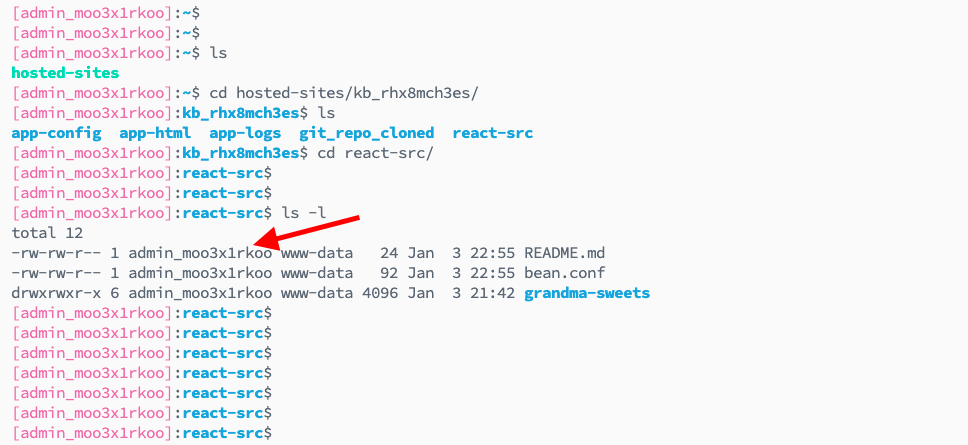
Currently, permissions are reset to admin user. You'll see files owned by the admin user (with admin_ prefix) and group www-data.
Step 5: Reset Permissions to App System User
To set permissions to app system user:
- Select App System User: Select "App System User" from the dropdown.
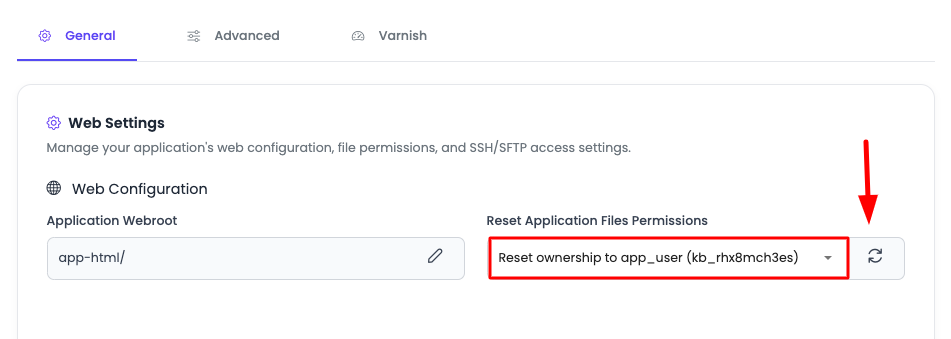
- Click Reset Permissions: Click on the "Reset Permissions" button to reset permissions to this user.
- Wait for Update: The system will update file ownership to the app system user.
Step 6: Verify Permissions (App System User)
-
SSH into Server: Connect to your server using SSH.
-
Navigate to Application Directory: Change to your application's source directory:
cd /home/admin/hosted-sites/<app_system_user>/<app_type>-src -
Check Permissions: Run the command again:
ls -l -
View Updated Permissions: Now check the permissions to see the updated ownership.
You'll now see files owned by the app system user and group www-data.
Understanding Application Directory Structure
Directory Types Based on Application
The location where permissions are updated depends on your application type:
Apps Dependent on app-html Directory
For applications that depend on the app-html directory for web files:
- Permission Location: File permissions are updated in the
app-htmldirectory - Use Case: Applications that serve static files or have a separate web root
- Example Path:
/home/admin/hosted-sites/<app_system_user>/app-html
Source Code Based Applications
For source code based applications:
- Permission Location: Permissions are updated in the
<app-type>-srcfolder because this is the source code directory - Examples:
- React applications:
react-src - FastApi applications:
fastapi-src - Node.js applications:
node-src - Laravel applications:
app-html - Wordpress applications:
app-html
- React applications:
- Example Path:
/home/admin/hosted-sites/<app_system_user>/react-src
When to Use Each Ownership Type
Use Admin User When:
- You need maximum control over application files
- You're performing server-level maintenance
- You need to access files across multiple applications
- You're troubleshooting permission issues
- You need to modify system-level configurations
Use App System User When:
- You want to restrict access to a specific application
- Developers are accessing files through app-specific SSH/SFTP users
- You want to follow the principle of least privilege
- You're working in a multi-application environment
- You want to isolate application access
Best Practices
- Choose Appropriate Ownership: Select ownership type based on your access needs and security requirements
- Verify After Changes: Always verify permissions after resetting to ensure they're correct
- Consider Developer Access: If developers use app-specific SSH users, use app system user ownership
- Document Changes: Keep track of when and why you changed permissions
- Test After Changes: Test your application after changing permissions to ensure everything works correctly
- Regular Audits: Periodically check file permissions to ensure they haven't been changed unexpectedly
Troubleshooting
Permission Denied Errors
- Check Ownership: Verify that file ownership matches your access method (admin user vs. app system user)
- Verify Permissions: Use
ls -lto check current permissions - Check Directory Permissions: Ensure parent directories have correct permissions (typically 755)
- Group Ownership: Verify group is set to
www-datafor web server access
Files Not Accessible via Web
- Web Server Access: Ensure files have read permissions for the web server (group
www-data) - Directory Permissions: Check that directories are executable (755) for web server navigation
- Ownership Type: Verify ownership type allows web server access
Developer Access Issues
- App System User: If developers use app-specific SSH users, ensure permissions are set to app system user
- Sufficient Rights: Verify developers have sufficient rights on files they need to modify
- Write Permissions: Ensure directories where developers need to write have appropriate permissions
Verification Commands
Use these commands to verify permissions:
# Check current directory permissions
ls -l
# Check specific file permissions
ls -l filename.php
# Check directory permissions
ls -ld directoryname
# Check ownership
stat filename.php
Common Permission Scenarios
Scenario 1: Files Added via FTP/SFTP
Issue: Files uploaded via FTP/SFTP may not have correct permissions.
Solution: Reset permissions using the KloudBean dashboard to ensure proper ownership and permissions.
Scenario 2: Permission Denied After File Upload
Issue: After uploading files, you get "permission denied" errors.
Solution: Reset permissions to the appropriate ownership type (admin user or app system user) based on your access method.
Scenario 3: Developer Cannot Modify Files
Issue: Developer accessing via app-specific SSH user cannot modify files.
Solution: Reset permissions to app system user to grant appropriate access to app-specific users.
Next Steps
After successfully managing file permissions:
- Learn about Enabling SSH Access for application users
- Explore Uploading and Managing Files to work with application files
- Review Security and Performance Settings to optimize your application security