Connecting Git Repository
Learn how to connect your Git repository (GitHub, GitLab, or Bitbucket) to your KloudBean application for seamless code deployment. This guide walks you through the complete process of enabling Git integration, configuring SSH keys, and deploying your code.
Overview
KloudBean's Git integration allows you to connect your code repository directly to your application, enabling automated deployments and streamlined code management. Whether you're using a public or private repository, KloudBean provides a secure and efficient way to deploy your code changes.
Benefits of Git Integration
- Automated Deployments: Deploy code changes automatically when you push to your repository
- Version Control: Track and manage different versions of your application
- Secure Access: Use SSH keys for secure authentication with private repositories
- Branch Management: Deploy from specific branches of your repository
- Build Automation: Automatically build your application after pulling the latest code
Prerequisites
Before connecting your Git repository, ensure you have:
- A Git Repository: A repository hosted on GitHub, GitLab, or Bitbucket
- Repository Access: Appropriate permissions to access your repository (read access for public repos, write access for private repos)
- A KloudBean Application: An application created in your KloudBean account
- SSH Key Access (for private repositories): Ability to add SSH keys to your Git provider account
Connecting Your Git Repository
Step 1: Navigate to Application Settings
To begin connecting your Git repository:
- Log in to your KloudBean dashboard using your account credentials.
- Click on your application from the Applications list to navigate to the application administration page.
- Navigate to the "Code Delivery" tab in the application settings menu.
- Locate the "Git deployment" section - this is the first tab within the Code Delivery section.
- You will see a button labeled "Enable Git integration" - this is where you'll start the Git connection process.
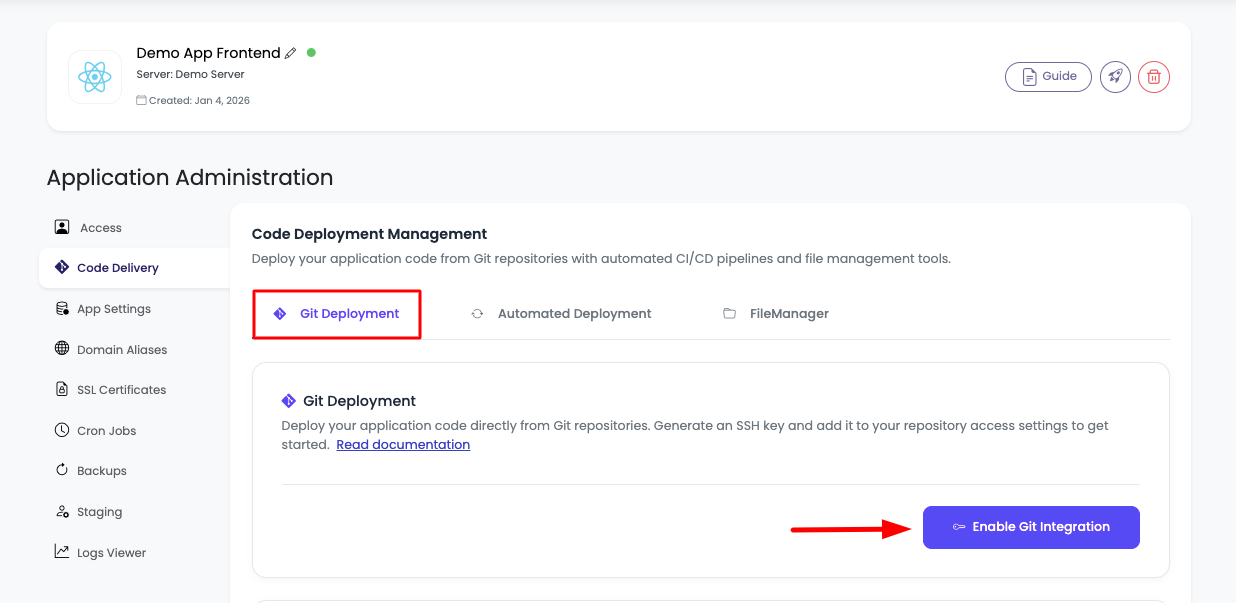
Step 2: Enable Git Integration
Once you're in the Git deployment section:
- Click on "Enable Git integration" to activate Git functionality for your application.
- SSH Key Generation: This action will automatically create a public SSH key for connecting to your Git repository. This key is essential if your repository is private, as it allows KloudBean to securely access your code.
- Key Purpose: The SSH key enables secure authentication between KloudBean and your Git provider (GitHub, GitLab, or Bitbucket) without requiring you to store passwords or tokens.
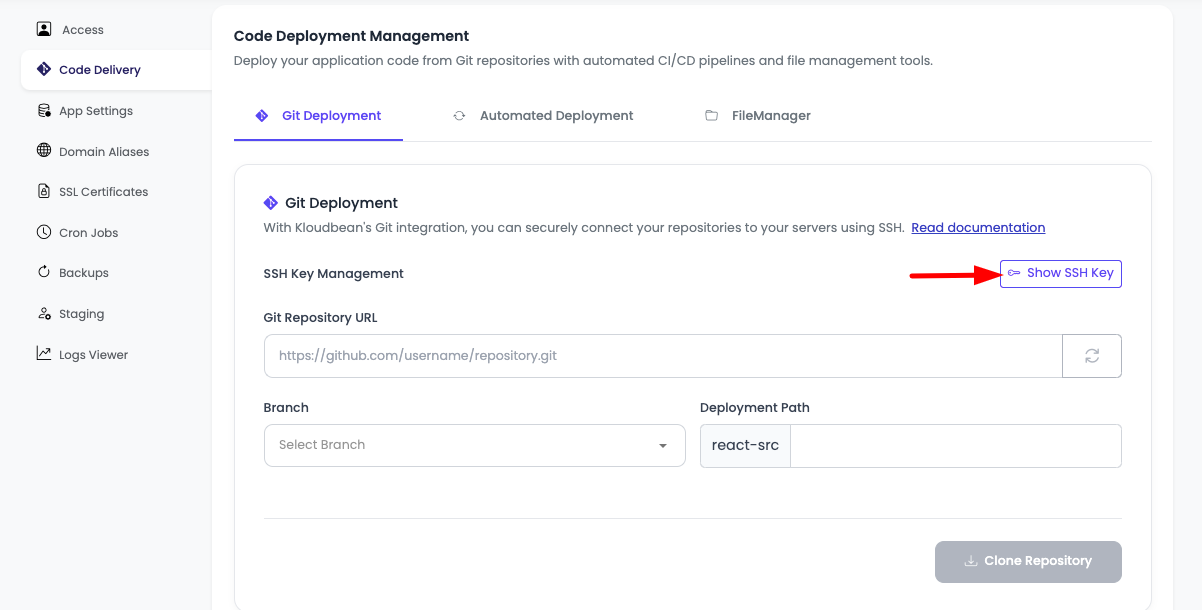
Step 3: View and Copy SSH Key
After enabling Git integration, you can view and copy your SSH public key:
- Click on "Show SSH key" button to display your application's public SSH key.
- The SSH key will be displayed in a text field or modal window.
- Copy the SSH key by clicking the copy button provided. This will copy the entire key to your clipboard, ready to be added to your Git provider account.
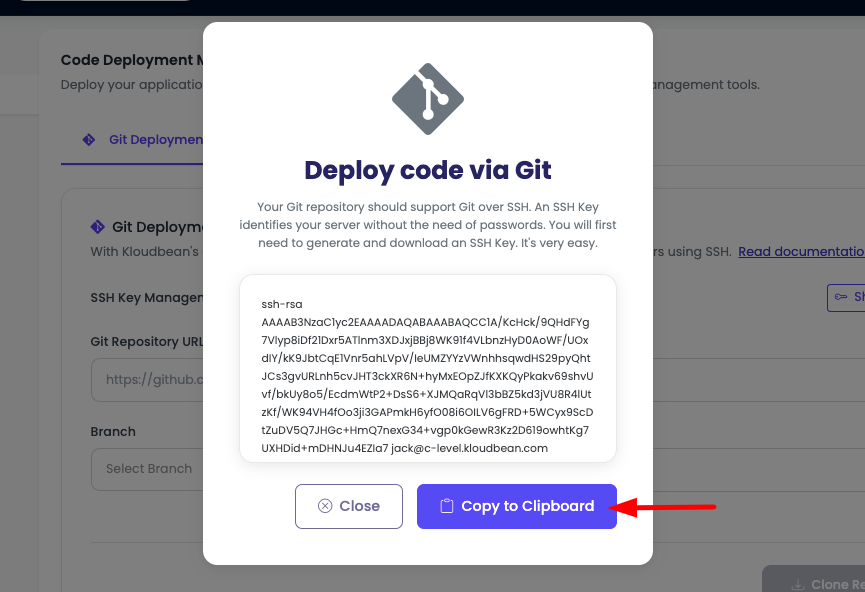
Important Notes:
- Each KloudBean application has its own unique SSH key
- Keep this key secure and only add it to repositories you trust
- The key is specific to this application and cannot be used for other applications
Step 4: Deploy SSH Key to Your Git Provider
Now that you have copied your SSH key, you need to add it to your Git provider account. The process varies slightly depending on your Git provider.
For GitHub
- Navigate to GitHub: Go to your GitHub account and click on your profile icon in the top right corner.
- Access Settings: From the dropdown menu, select "Settings".
- Open SSH Keys Section: In the left sidebar, locate and click on "SSH and GPG keys".
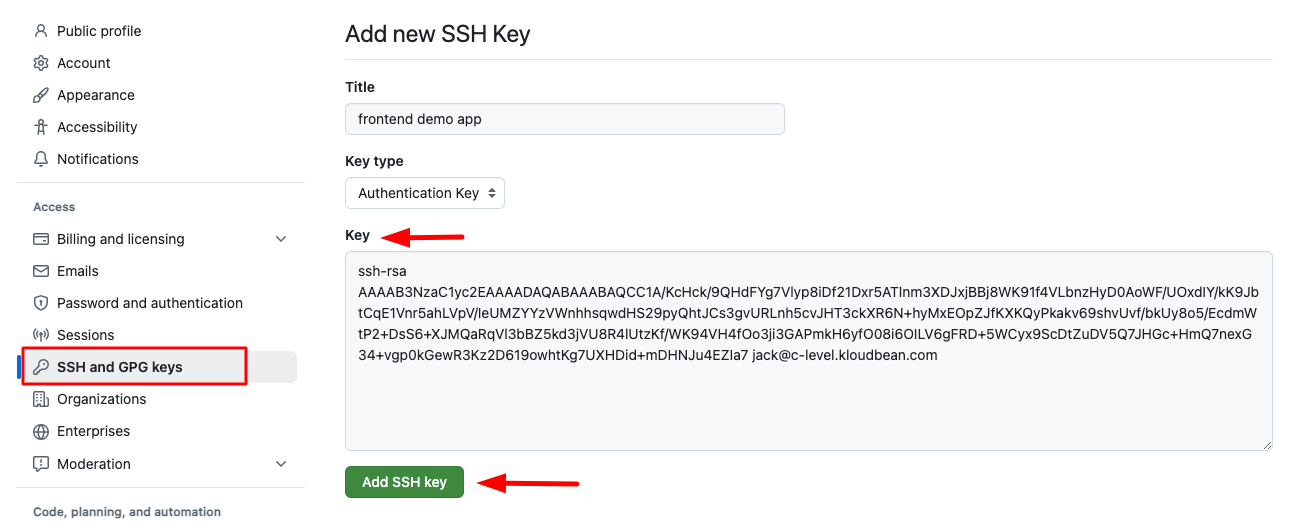
- Add New Key: Click on the "New SSH key" button to add a new SSH key.
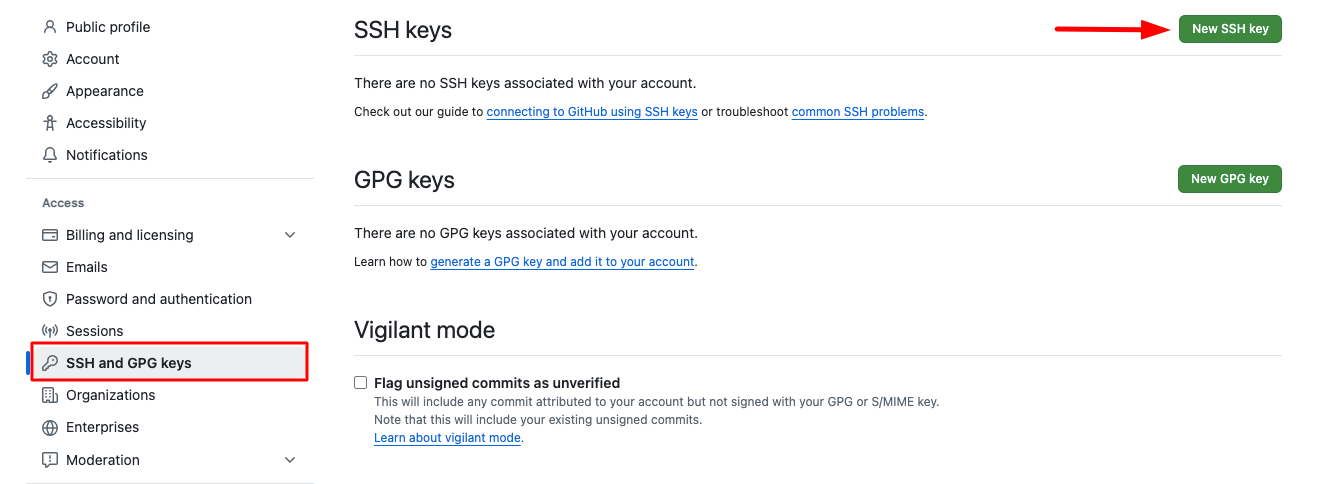
- Enter Key Details:
- Title: Enter a descriptive title for this key (e.g., "KloudBean App - [Your App Name]")
- Key: Paste the SSH key you copied from KloudBean into the "Key" field
- Save the Key: Click "Add SSH key" to save and activate the key.
- Verification: Once added, you have successfully configured the SSH key to connect your private GitHub repository with KloudBean.
For GitLab
- Navigate to GitLab: Go to your GitLab account and click on your profile icon.
- Access Preferences: Select "Preferences" from the dropdown menu.
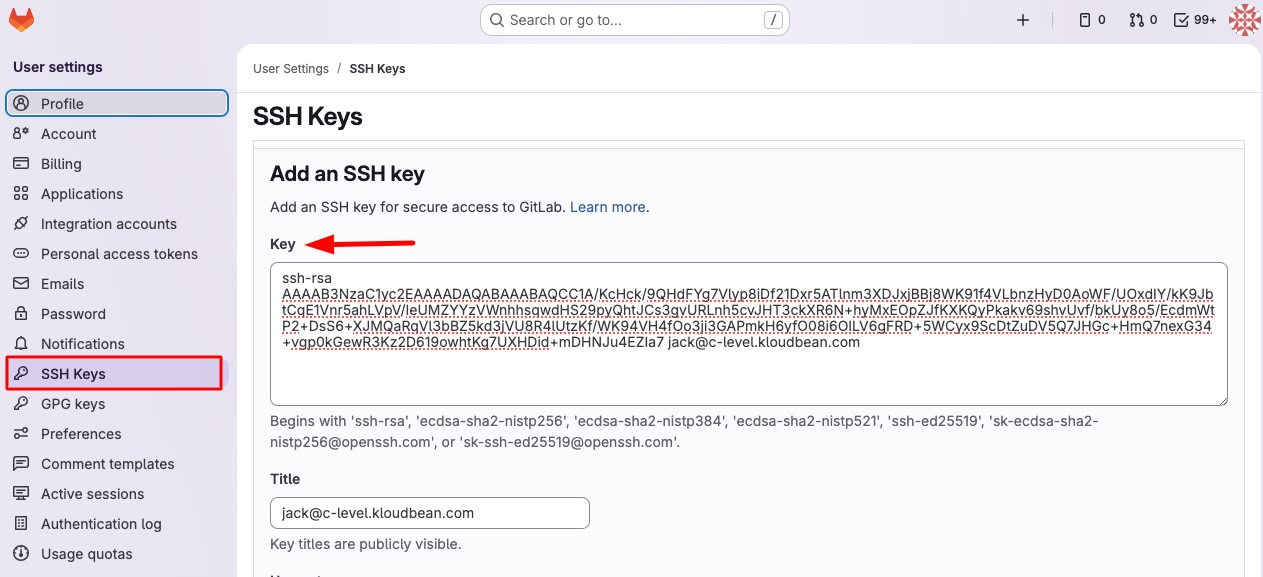
- Open SSH Keys Section: In the left sidebar, click on "SSH Keys".
- Add New Key: Click on "Add new key" button.
- Enter Key Details:
- Key: Paste the SSH key you copied from KloudBean into the "Key" field
- Title: Optionally add a descriptive title for this key
- Save the Key: Click "Add key" to save and activate the SSH key.
Step 5: Copy Your Repository URL
After adding the SSH key to your Git provider, you need to copy your repository URL:
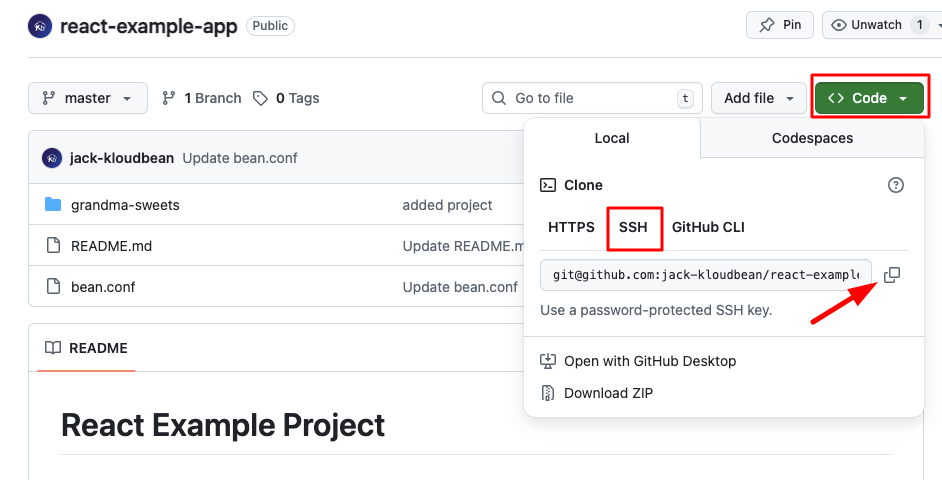
- Navigate to your repository on GitHub, GitLab, or Bitbucket.
- Click on the "Code" button (or equivalent) to view repository URLs.
- Select the appropriate URL:
- For Public Repositories: Copy the HTTPS URL - this is simpler and doesn't require SSH key authentication.
- For Private Repositories: Copy the SSH URL - this uses the SSH key you just added for secure authentication.
URL Format Examples:
- HTTPS:
https://github.com/username/repository.git - SSH:
[email protected]:username/repository.git
Step 6: Connect Repository to KloudBean
Now that you have your repository URL, return to KloudBean to complete the connection:
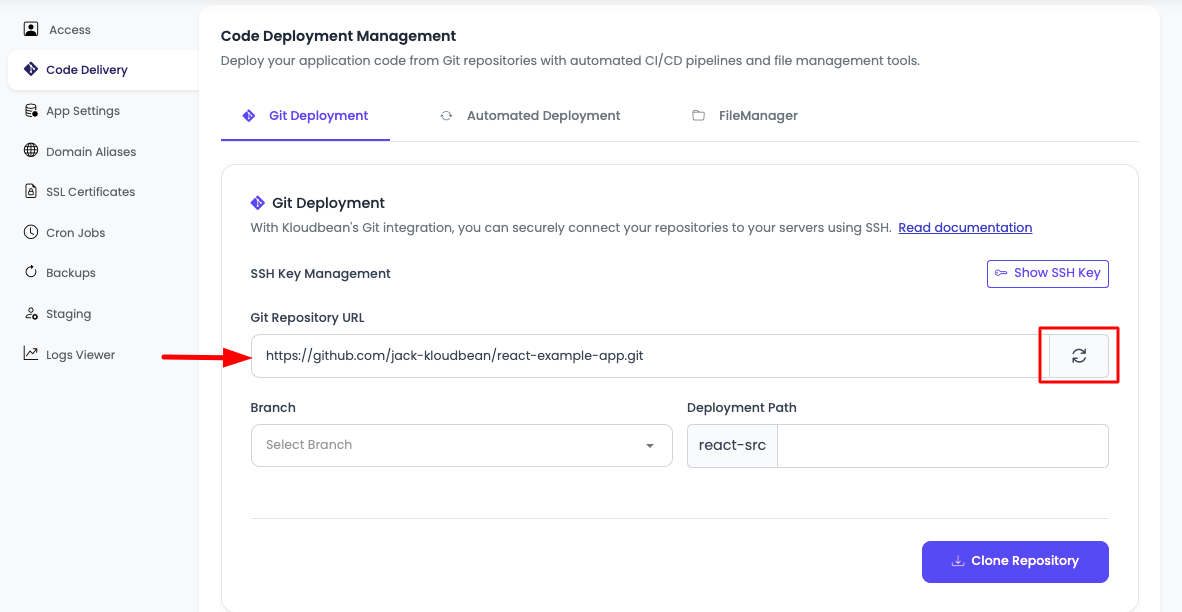
- Return to KloudBean: Go back to your KloudBean application's Git deployment section.
- Paste Repository URL: In the "Git repository URL" field, paste the repository URL you copied (HTTPS for public repos, SSH for private repos).
- Fetch Branches: Click on the fetch icon (or "Load" button) next to the URL field. This action will connect to your repository and retrieve all available branches.
-
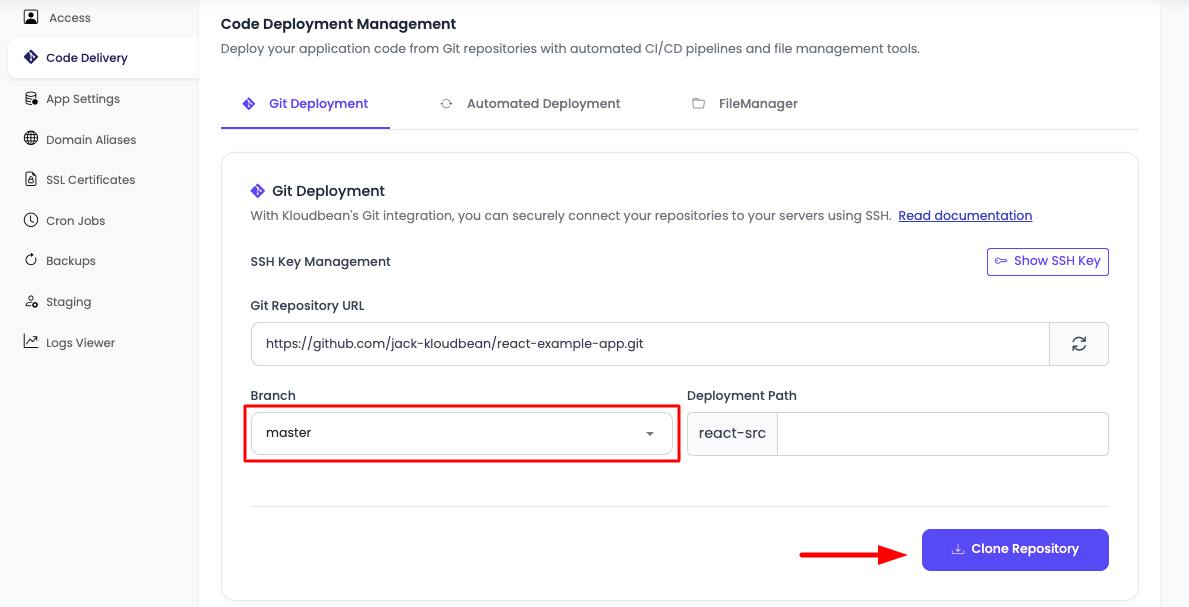
Select Branch: Once branches are loaded, you'll see a dropdown list of all available branches. Select the branch you want to deploy (typically
main,master, or your production branch). -
Configure Deployment Path (Optional):
- You can optionally change the code deployment path, which will create a new directory in your application's deployment folder.
- This is useful if you want to deploy to a specific subdirectory or organize multiple deployments.
-
Clone Repository: After selecting your branch, click on "Clone repository" to initiate the cloning process. This will download your repository code to your KloudBean application.
Congratulations! You have successfully cloned your repository to your KloudBean application. Your code is now available in your application's deployment directory.
Step 7: Pull and Deploy Code
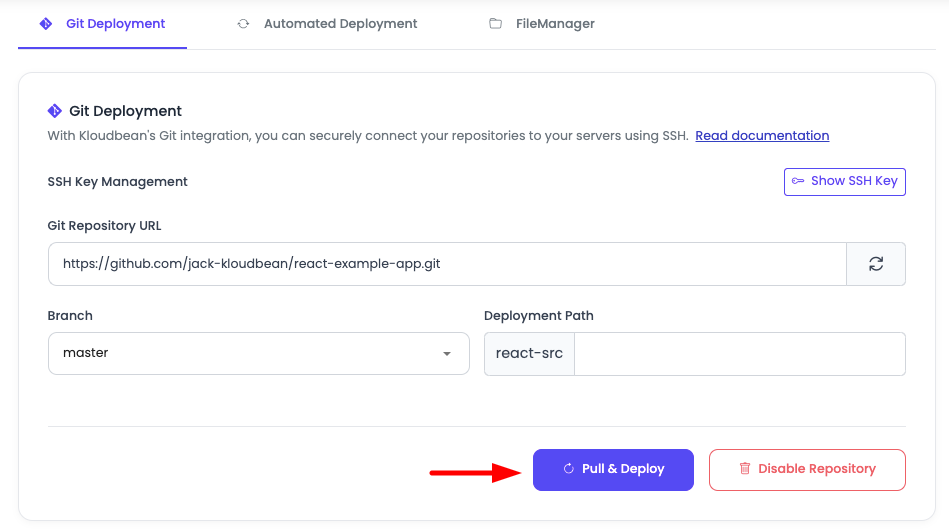
After cloning your repository, you can pull the latest changes and deploy your application:
- Access Pull & Deploy: Click on the "Pull & Deploy" button in the Git deployment section.
-
What This Action Does:
- Pulls Latest Code: Retrieves the latest changes from your selected branch
- Initiates Build Process: If your application is build-dependent (requires compilation, npm build, etc.), KloudBean will automatically initiate the build process
- Deploys Application: After a successful build (if required), your application will be deployed with the latest code
-
Build-Dependent Applications:
- Applications like React, Angular, Vue.js, Next.js, or any framework requiring a build step will automatically trigger the build process
- The build process runs the appropriate build commands based on your application type
- You can monitor the build progress in the deployment logs
Understanding Git Integration Features
Public vs. Private Repositories
- Public Repositories: Can be connected using HTTPS URLs without SSH key configuration
- Private Repositories: Require SSH key authentication for secure access
Branch Selection
- You can deploy from any branch in your repository
- Common branches include
main,master,develop, or custom branch names - You can switch branches at any time by selecting a different branch and cloning again
Deployment Path
- The default deployment path is your application's root directory
- You can specify a custom path if your application code is in a subdirectory
- Useful for monorepos or applications with specific directory structures
Best Practices
- Use SSH Keys for Private Repos: Always use SSH keys for private repositories to ensure secure access
- Branch Strategy: Use separate branches for development, staging, and production environments
- Regular Updates: Use "Pull & Deploy" regularly to keep your application up-to-date with the latest code changes
- Monitor Builds: Check build logs if your application fails to deploy after pulling new code
- Key Management: Keep track of which SSH keys are associated with which applications for easier management
Troubleshooting
SSH Key Issues
- Key Not Working: Ensure the SSH key was correctly copied (no extra spaces or line breaks)
- Permission Denied: Verify the SSH key has been added to your Git provider account
- Key Already Exists: If you see an error about duplicate keys, check if the key was already added
Repository Connection Issues
- URL Format: Ensure you're using the correct URL format (HTTPS for public, SSH for private)
- Repository Access: Verify you have the necessary permissions to access the repository
- Network Issues: Check your internet connection if the fetch operation fails
Deployment Issues
- Build Failures: Review build logs to identify compilation or dependency errors
- Branch Not Found: Ensure the branch name is correct and exists in your repository
- Deployment Path Errors: Verify the deployment path is correct and accessible
Next Steps
After successfully connecting your Git repository:
- Learn about Enabling Auto Deployment to automate deployments on every push
- Explore Managing Application Domains to configure custom domains
- Review Security and Performance Settings to optimize your application