Flask Deployment
Deploy Python Flask applications in a production-ready environment on KloudBean.
Overview
On KloudBean, you get a complete production-ready stack to build and host high-performance Flask applications.
You get:
- Git integration to pull your code on the server
- SSH access to the server to run commands manually and using ADM tool for quick deployment
- File Manager access to add, update and manage files with ease
- Optimized and configured Gunicorn for serving your Flask application
Launching New Flask Application
If you already have a server and want to launch an app on it, go to Applications → Add Application and add a Flask app on an existing server.
In this example, we will create a brand new server.
In order to launch your first Flask app on a new server, navigate to the server provision page:
- Select Cloud Provider (your choice)
- Select Application (Flask)
- Select Datacenter with nearest location
- Add Application Name
- Add Server Name
- Select Server size depending on needs (for Flask build minimum recommended size is 2-4GB)
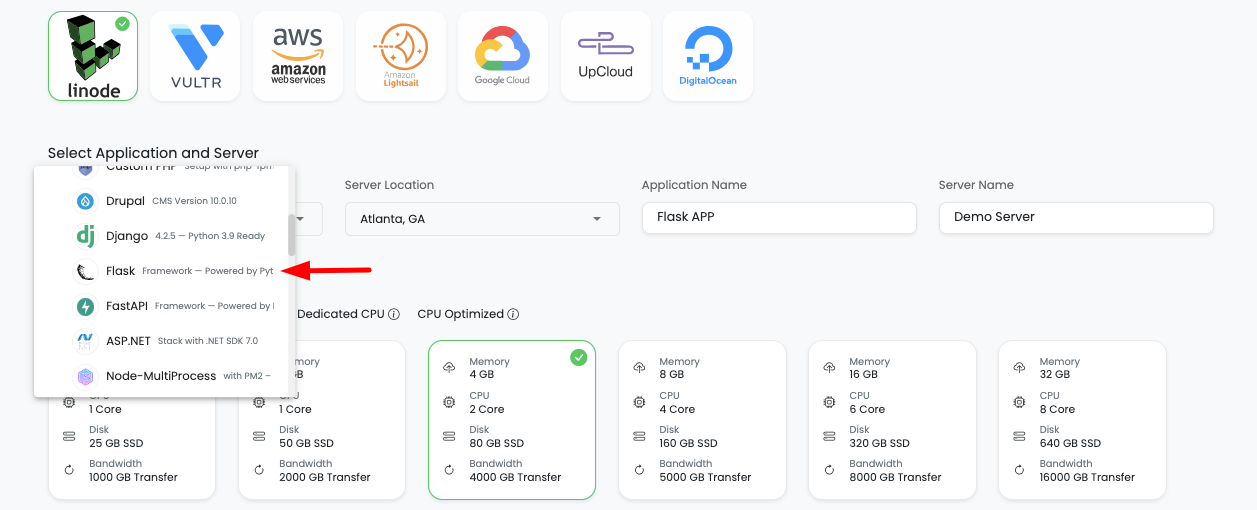
Click on Launch button and proceed with the payment process (trial or payment).
Once payment is completed, server with Flask app provisioning will be initiated.
Wait for a while; it will take 5-7 minutes to create your server, configure and deploy a high-performance web stack.
By default, on a new server you will get the following stack versions:
- Python > 3.11
- Flask (latest)
- Gunicorn
- MariaDB > 10.6 (optional)
Accessing Application Administration
Once your server is ready, in order to access your Flask app, select "Apps" from the header menu to go to the Applications page.
On this page, you will see your application in active status.
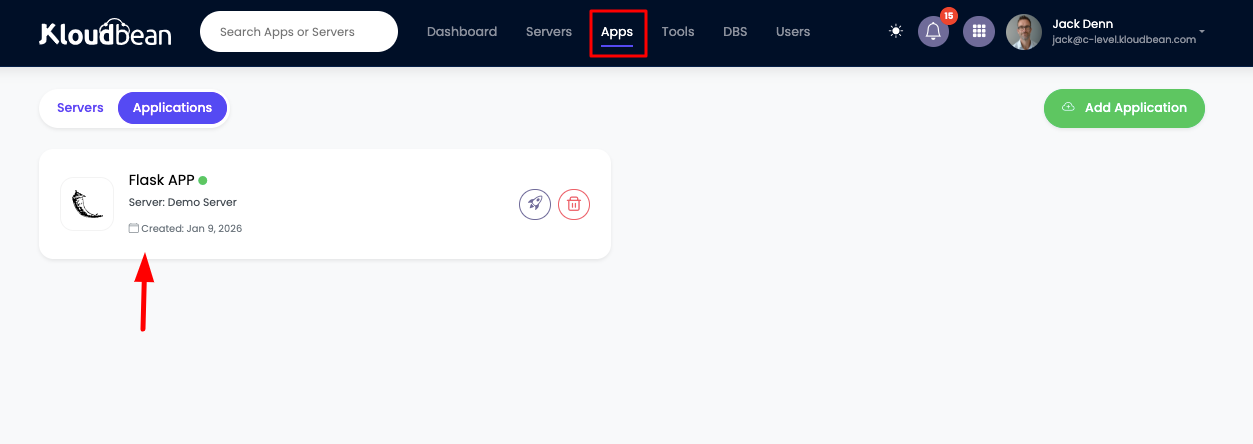
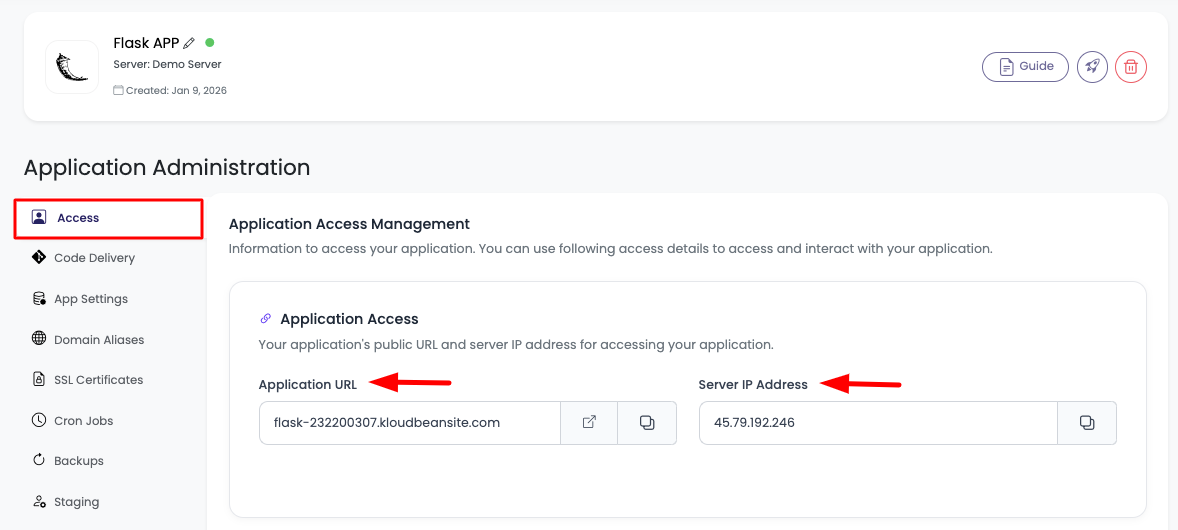
Click on it to navigate to "Application Administration" > "Access" section.
On this section, you will see:
- Application default access URL
- Server public address to point your custom domain to it
Deploying Your Code
The next step is to deploy your code.
In order to deploy your code, navigate to the "Code Delivery" tab.
Here, on the first tab → "Git deployment":
- Click on "Enable Git Integration"
- Copy SSH public key and add it to your SCM provider (GitHub, GitLab)
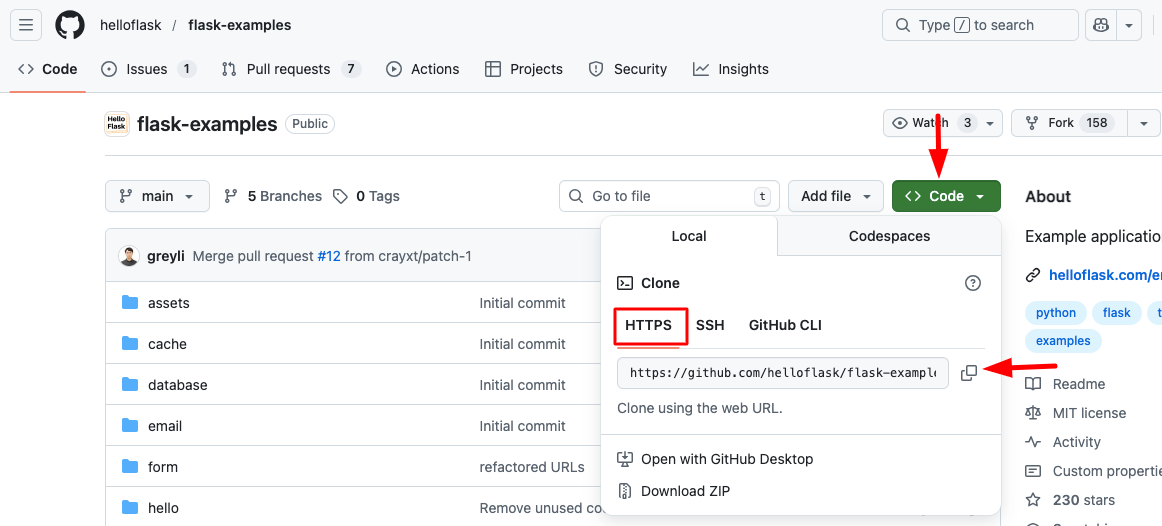
- Copy your repo URL and add it here in "Git Repository URL", select branch and "Clone Repository"
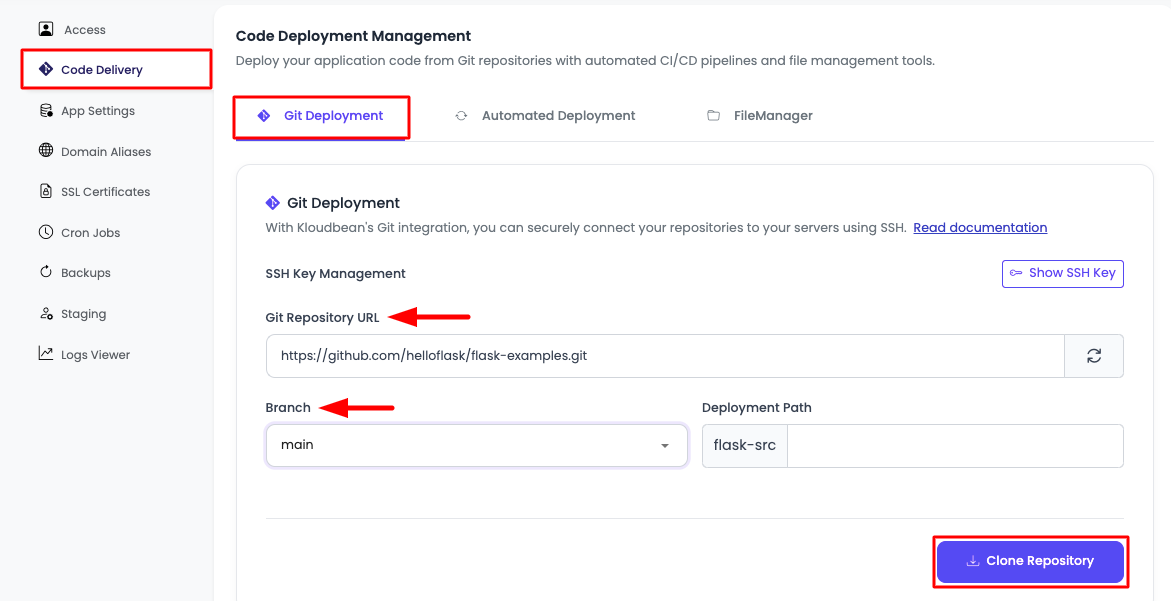
In this example, we're going to deploy an example Flask app:
https://github.com/helloflask/flask-examples.git
Read the detailed guide on connecting Git.
Once the repo is cloned, the next step is to run the deployment. Click on "Pull & Deploy".
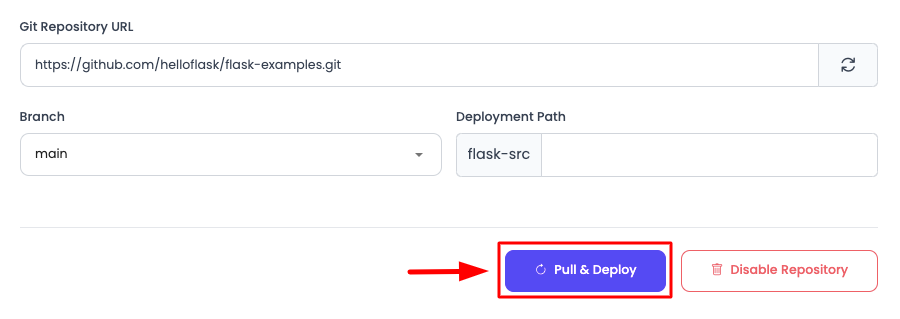
Once you click, it will initiate the build process automatically by doing the following at the backend:
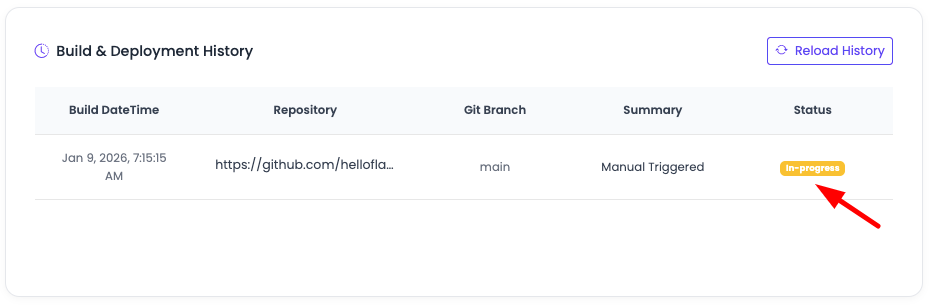
- Take latest repo pull
- Adding
bean.confto add Flask basic configuration - Installing packages
- Updating Gunicorn configs
- Starting workers
Updating bean.conf Script
Application basic info is mentioned in a file named bean.conf.
It is important to give the app name with this convention: <your-app-folder>:app
Also specify:
- App directory (mostly
/) - Number of workers
In order to create this file, go to the flask-src directory and create this file. If the file already exists, update the content.
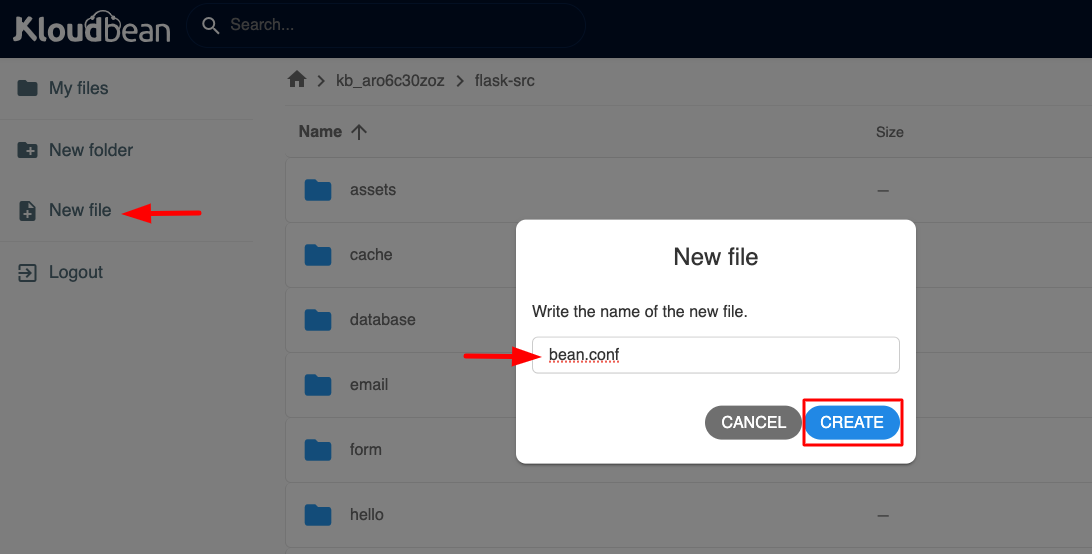
Add File Using File Manager
Add the bean.conf file using File Manager:
Or Using Command Through Shell
nano /home/admin/hosted-sites/<app_system_user>/flask-src/bean.conf
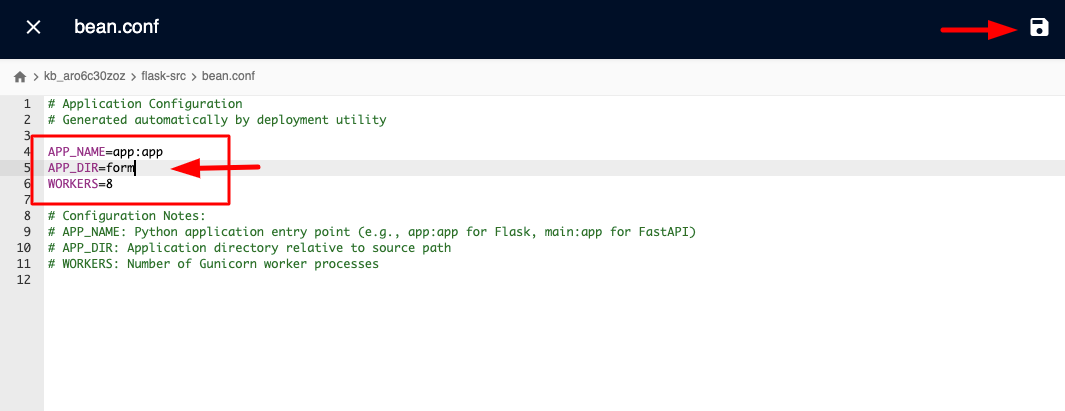
And add the following content. In this example, we're adding basic configuration:
APP_NAME=<your-app-folder>:app
APP_DIR=/
WORKERS=8
Updating/Adding Environment (.env) File
If you need to add or update the .env file, you can access it using File Manager or optionally using shell.
Navigate to the third tab "FileManager" and click "Launch FileManager" button to open it in a new tab.
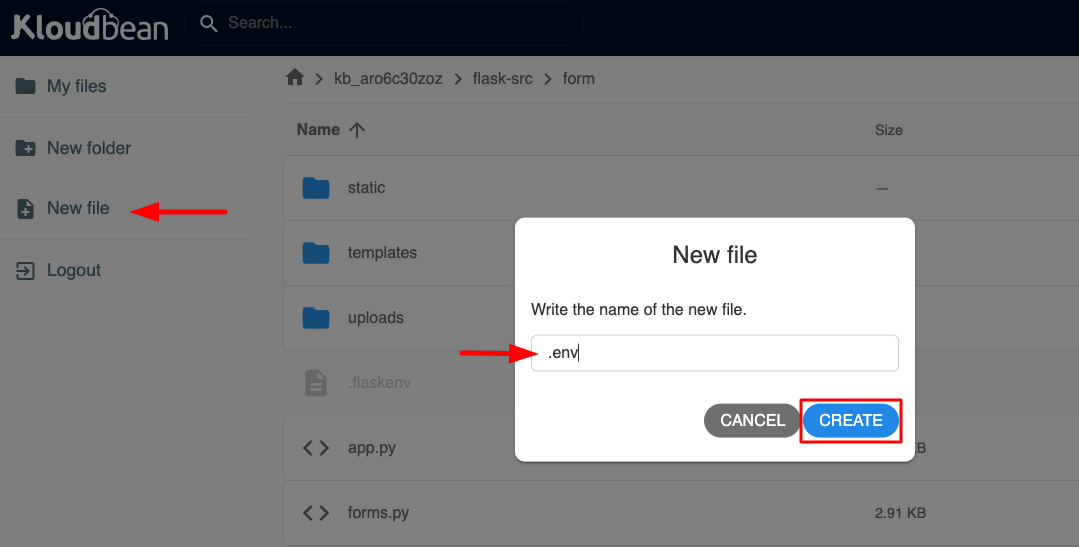
Once you are in File Manager, in the flask-src directory, you can create a new file .env by clicking on "New file" from the left sidebar.
Give the file name and click "Create".
It will open a new file in the editor. Add your required environment variables. For example:
APP_URL=https://flask-232200305.kloudbeansite.com
DB_HOST=localhost
DB_NAME=kb_aro6c30zoz
DB_USERNAME=kb_aro6c30zoz
DB_PASSWORD=31vYF9Dc65gHbV742m
In order to get database access credentials, read the detailed guide on Viewing Database Credentials.
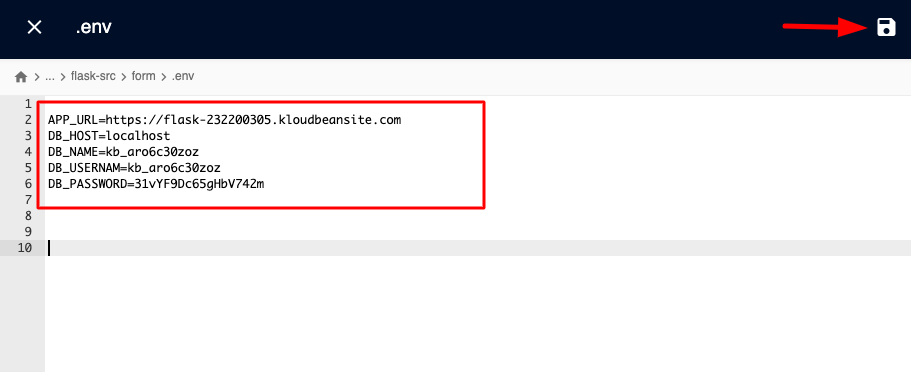
Once updated, click on the "Save" icon on the top right corner of the editor, and it will be saved.
Viewing Build Logs
If you see your build failed or you need to see build and installation logs, click on your current build and a prompt will open to view the logs.
Once your application is started, you can access it from the access URL:
"Application Administration" → Access → Access URL
If you are seeing 503, that means your application is not up and has some errors.
In order to view application logs:
- You can view logs using File Manager
- Or by SSH into the server
Go to directory: /home/admin/hosted-sites/<app_system_user>/app-logs
Important: It is important to check your application logs if your site is responding with a 503 gateway error. It shows that the application is not running.
In this directory, application logs are being added in the following log files:
- app.info.log → information logs
- app.error.log → error logs
You can open these files using File Manager to view the errors.
Deployment Using ADM Tool (Application Deployment Manager)
Application Deployment Manager (ADM) is one of KloudBean's features that enables you to deploy your app quickly by just executing one command. It supports all Flask and Python-based applications.
In order to perform deployment using the ADM tool, you have to access your server using shell.
Read the detailed guide on how to SSH server on KloudBean.
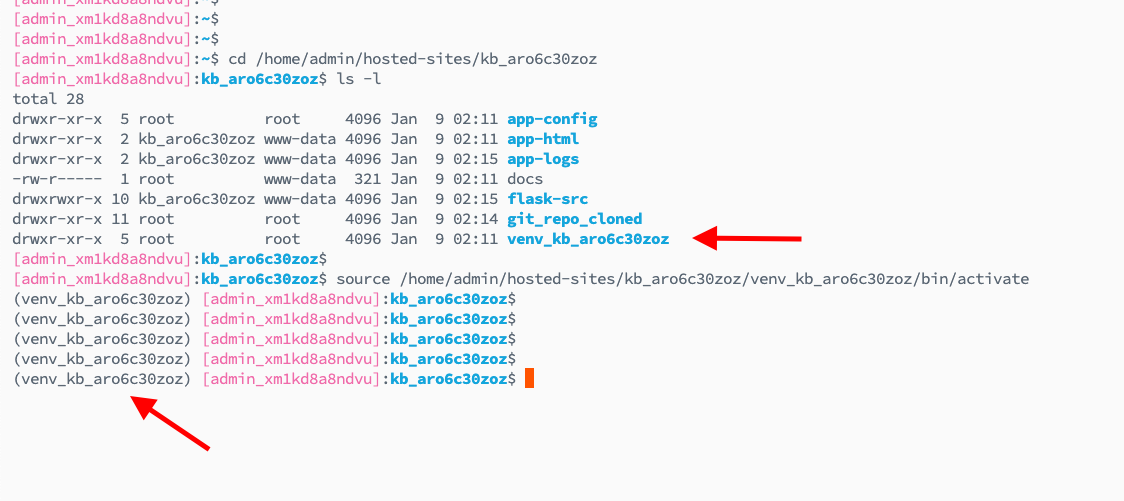
Optionally Enable Python Virtual Environment
When you launch any Python-based framework on KloudBean, you get automatically configured a virtual Python environment with each app. You don't have to manually create one.
In order to enable the virtual environment, run this command:
source /home/admin/hosted-sites/<app_system_user>/venv_<app_system_user>/bin/activate
And your virtual environment will be activated.
Once you are connected to the server, run the following ADM command:
sudo adm
or
sudo adm <app_system_user>
→ to directly execute for the required application.

If you run this command without app_system_user, then you will have to select the app by providing its number in the prompt and click hit enter.
It will start the deployment process with the logs and progress details on the shell screen.
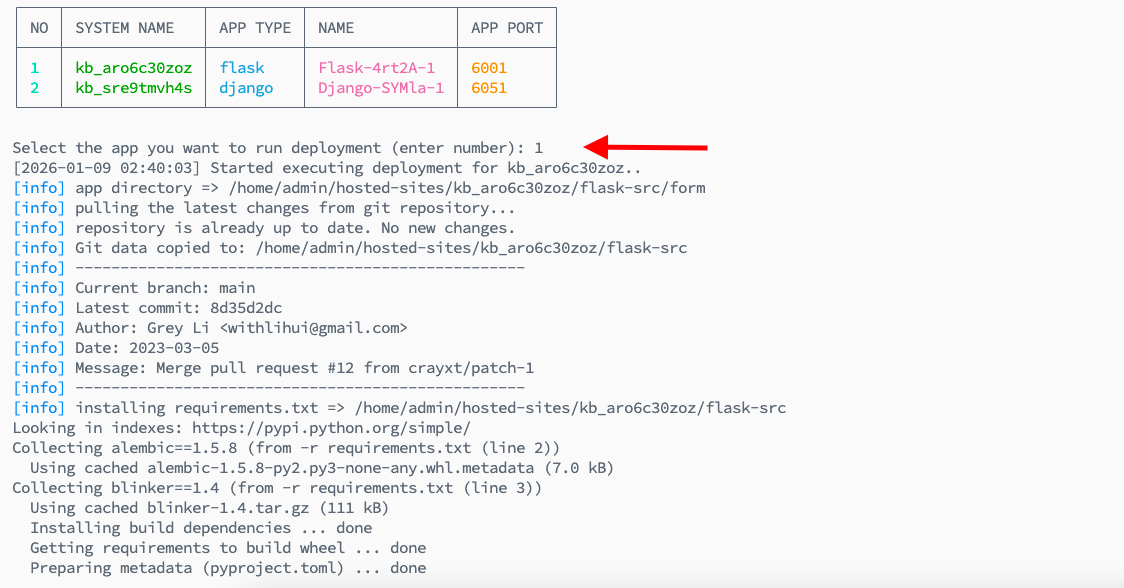
Information: While executing deployment through ADM, you will see the port as well to get to know on which port the app is running.
Handling Build Errors
If you are seeing the build has failed, you can see build logs.
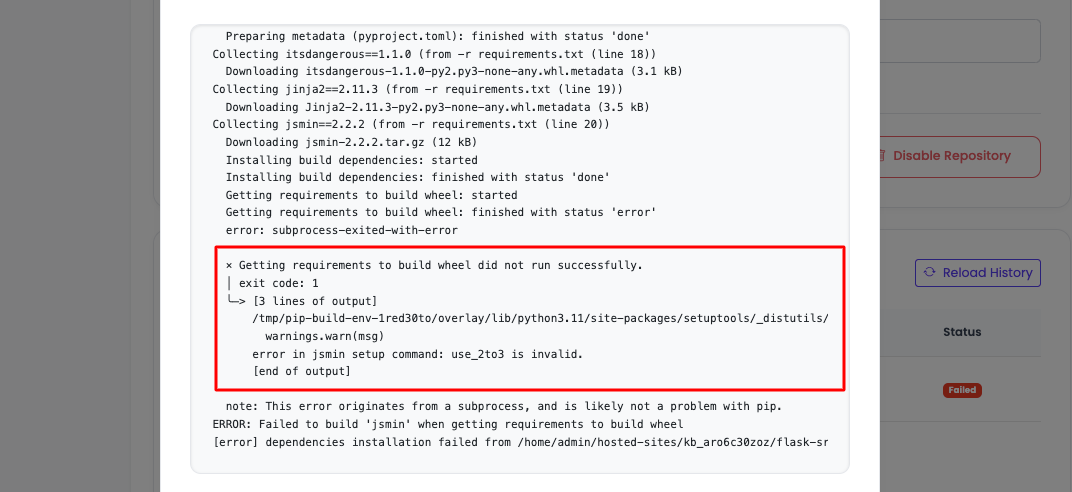
While executing ADM, you might see the app failed. Carefully watch the error and try to fix it. For example, in this case, you might face this error:
× Getting requirements to build wheel did not run successfully.
│ exit code: 1
╰─> [3 lines of output]
/tmp/pip-build-env-1red30to/overlay/lib/python3.11/site-packages/setuptools/_distutils/dist.py:289: UserWarning: Unknown distribution option: 'test_suite'
warnings.warn(msg)
error in jsmin setup command: use_2to3 is invalid.
[end of output]
This type of error typically occurs when a package in your requirements.txt has compatibility issues with the current Python version or setuptools. To fix this:
- Update the problematic package: Check if there's a newer version of the package that's compatible with Python 3.11
- Remove incompatible packages: If the package is not essential, consider removing it or finding an alternative
- Pin package versions: Specify compatible versions in your
requirements.txtto avoid conflicts - Update setuptools: Ensure you're using a recent version of setuptools in your requirements
Once the error is fixed, then run the build again using "Pull & Deploy" or using the ADM tool from shell.
Next Steps
- Learn how to enable automated deployment
- Add custom domain
- Install SSL certificates for your site