Managing Server Packages and Services
Learn how to manage server packages and services on your KloudBean server. KloudBean provides you control over the server stack components where you can perform various changes to manage your server infrastructure.
Overview
KloudBean provides you control over the server stack components where you can perform these changes:
Service Management
Handle Services State:
- Restart: Restart services to apply configuration changes or resolve issues
- Stop/Start: Control service execution (with restrictions for critical services)
- View Resource Consumption: Monitor memory (mem), CPU, and threads usage for each service
Package Handling
Package Operations:
- Change Package Version: Update packages to different versions
- Install Package: Install new packages from available list
- Remove Package: Remove packages that are not system-dependent
Important Restrictions
Package Removal Restrictions
KloudBean only allows you to remove those packages which are not system-dependent. Some critical components like Nginx, MariaDB, Nginx you cannot remove them.
What This Means:
- System-Dependent Packages: Critical system packages cannot be removed
- Protected Components: Core server components are protected
- Safety Measure: Prevents accidental removal of essential services
- System Stability: Ensures server stability and functionality
Examples of Protected Packages:
- Nginx: Web server (cannot be removed)
- MariaDB: Database server (cannot be removed)
- Apache: Web server (cannot be removed)
- PHP: Core runtime (cannot be removed)
- Other Critical Components: System-dependent packages
Service Control Restrictions
Similarly, in services, you cannot stop Nginx, Apache, MariaDB, but you can only restart them.
What This Means:
- Critical Services: Core services cannot be stopped
- Restart Only: Critical services can only be restarted
- Optional Stop: Non-critical services can be stopped
- System Protection: Prevents accidental service shutdown
Examples of Protected Services:
- Nginx: Cannot be stopped (restart only)
- Apache: Cannot be stopped (restart only)
- MariaDB: Cannot be stopped (restart only)
- Other Critical Services: Core system services
Why These Restrictions:
- System Stability: Prevents breaking the server
- Service Availability: Ensures critical services remain available
- Managed System: KloudBean manages the system and keeps it operational
- Safety First: Protects against accidental misconfigurations
Prerequisites
- An active KloudBean server
- Access to server administration settings
- Understanding of service and package management
Accessing Service and Package Management
Step 1: Navigate to Service Tab
In order to access these settings:
- Log in to your KloudBean dashboard
- Navigate to Server Administration: Open the server administration page for your desired server
- Go to "Service" Tab: Click on the "Service" tab in the server settings menu
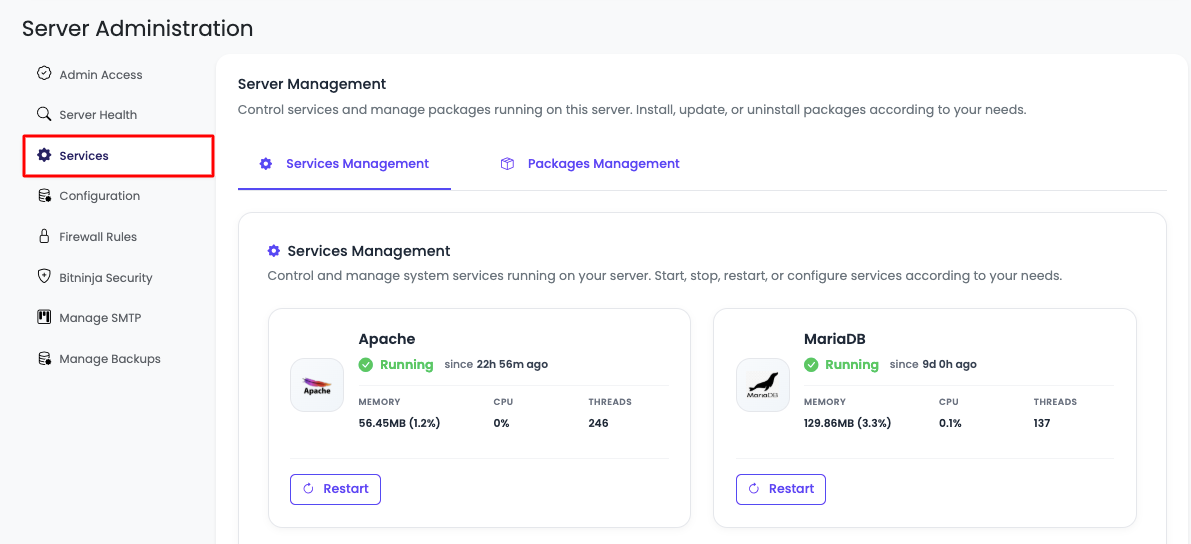
Service Management
Step 2: Access Service Management
In the first tab, you will see "Service Management".
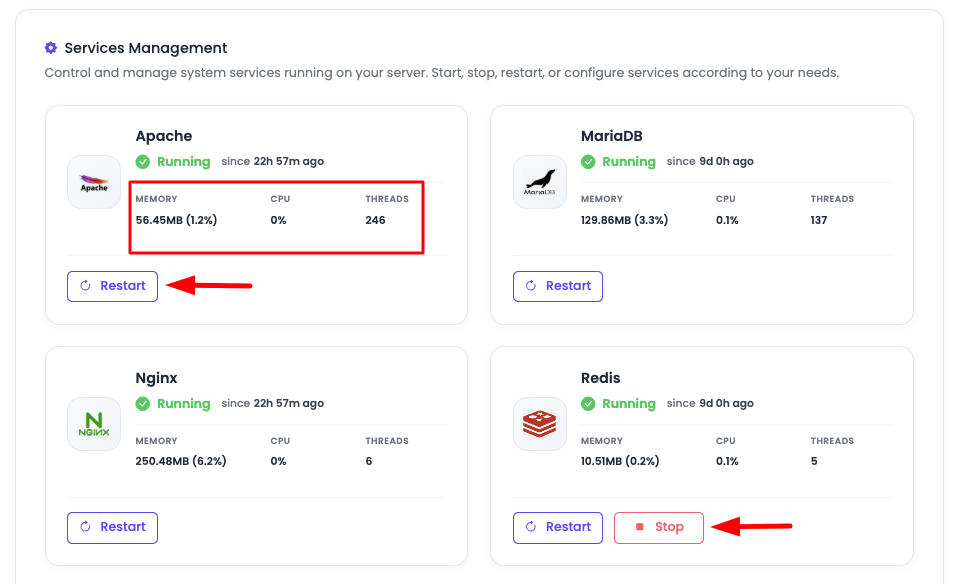
Service Management Overview
Service Management will list you all the critical installed services, along with its status and resource consumed by it.
Information Displayed:
- Service Name: Name of the service (e.g., Nginx, Apache, MariaDB, PHP-FPM)
- Status: Current status (Running, Stopped, Failed)
- Resource Consumption:
- Memory (RAM): Memory usage by the service
- CPU: CPU usage percentage
- Threads: Number of threads/processes
Why Resource Utilization Details Are Helpful
Performance Monitoring:
- Identify Resource Hogs: Quickly identify services consuming excessive resources
- Performance Optimization: Understand which services need optimization
- Capacity Planning: Plan server scaling based on actual resource usage
- Troubleshooting: Diagnose performance issues by identifying resource-intensive services
Resource Management:
- Memory Management: Monitor memory usage to prevent out-of-memory errors
- CPU Monitoring: Track CPU usage to identify bottlenecks
- Thread Analysis: Understand process/thread counts for each service
- Load Balancing: Make informed decisions about resource allocation
Service Health:
- Health Indicators: Resource usage can indicate service health
- Anomaly Detection: Unusual resource consumption may indicate issues
- Optimization Opportunities: Identify services that could be optimized
- Capacity Warnings: Early warning when services approach resource limits
Available Operations
Here you have options to:
Check Resource Utilization:
- View detailed resource consumption for each service
- Monitor memory, CPU, and thread usage
- Track resource trends over time
- Identify services with high resource usage
Restart Service:
- Restart any service to apply configuration changes
- Resolve service issues by restarting
- Refresh service state
- Apply updates or fixes
Optional Stop Service:
- Stop non-critical services when needed
- Free up resources by stopping unused services
- Temporarily disable services for maintenance
Critical services (Nginx, Apache, MariaDB) cannot be stopped.
Additional Operations:
- Disabling Services: Disable services from starting on boot
- Purging Varnish: Clear Varnish cache or disable Varnish service
- Service Configuration: Access service-specific settings
- Service Logs: View service logs for troubleshooting
Viewing All Resources
Scroll down to see all the resources:
- Complete list of all services
- Detailed resource consumption for each
- Service status and health indicators
- Available operations for each service
Package Management
Step 3: Access Package Management
In the second tab, you will see "Package Management".
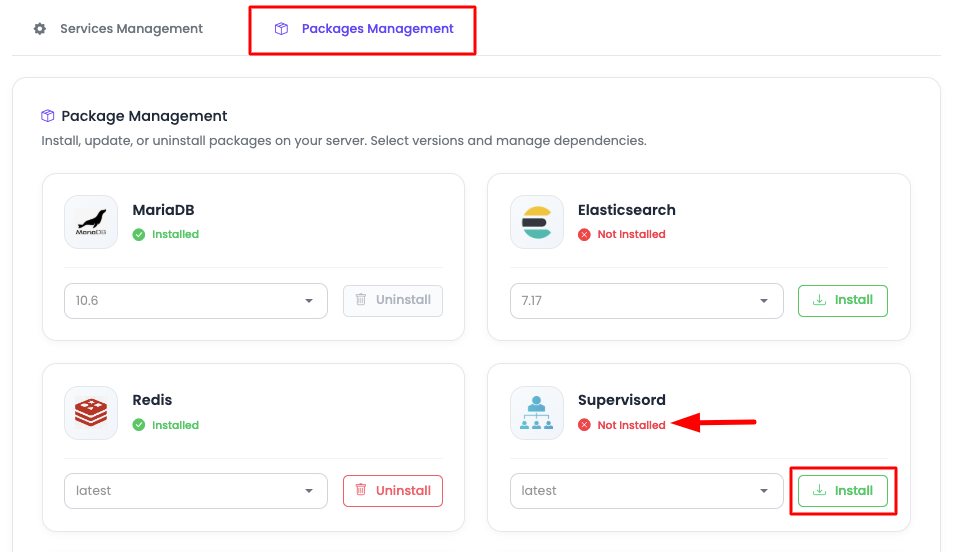
Package Management Overview
Package Management - On this tab, you will see all the available critical packages, where you have options to:
Change Package Version:
- Update packages to newer versions
- Downgrade packages if needed
- Switch between available versions
- Important: Be careful when changing versions (see warnings below)
Optionally Remove Package:
- Remove packages that are not system-dependent
- Free up disk space by removing unused packages
- Clean up unnecessary packages
System-dependent packages cannot be removed.
Install Listed Package:
- Install packages from the available list
- Add new functionality to your server
- Install required dependencies
For packages not in the list, contact support.
Important Warnings About Version Changes
Critical Warning
If you are going to change version of any package, be careful when doing it, as it could break your web application.
Why Correct Version Matters
Application Compatibility:
- Framework Requirements: Applications are built for specific package versions
- API Compatibility: Different versions may have different APIs
- Breaking Changes: Version updates may introduce breaking changes
- Dependency Conflicts: Version changes can cause dependency conflicts
System Stability:
- Service Interruption: Version changes may require service restarts
- Configuration Changes: New versions may require configuration updates
- Feature Changes: Features may be added, removed, or changed
- Bug Introductions: New versions may introduce new bugs
Risk Assessment:
- Production Impact: Version changes can impact production applications
- Downtime Risk: May cause temporary service unavailability
- Data Integrity: Incorrect versions may affect data handling
- Rollback Complexity: Rolling back may be complex or impossible
Version Change Risks
Without Proper Care:
- Application Breakage: Applications may stop working
- Feature Loss: Features may stop working or be removed
- Security Issues: Older versions may have security vulnerabilities
- Performance Degradation: New versions may perform worse
- Compatibility Issues: May break compatibility with other components
Best Practices:
- Test First: Always test version changes in staging first
- Read Changelog: Review what changed in the new version
- Backup First: Create backups before version changes
- Plan Downtime: Schedule version changes during maintenance windows
- Monitor Closely: Monitor applications after version changes
Language-Specific Considerations
PHP Version Changes
PHP Version Compatibility:
- Application Requirements: PHP applications are written for specific PHP versions
- Syntax Changes: Different PHP versions have different syntax requirements
- Extension Compatibility: PHP extensions must match PHP version
- Performance Impact: Different PHP versions have different performance characteristics
Common Issues:
- Deprecated Functions: Functions may be deprecated or removed
- Type System Changes: Type system changes between versions
- Error Handling: Error handling may change between versions
- Extension Availability: Some extensions may not be available in all versions
Recommendations:
- Check Compatibility: Verify application compatibility before upgrading
- Test Extensions: Ensure all PHP extensions are compatible
- Review Code: Review application code for deprecated features
- Gradual Upgrade: Consider gradual upgrades (e.g., 7.4 → 8.0 → 8.1)
Python Version Changes
Python Version Compatibility:
- Syntax Differences: Python 2 vs Python 3 have significant differences
- Library Compatibility: Python libraries are version-specific
- Package Managers: pip and package managers are version-dependent
- Virtual Environments: Virtual environments are tied to Python versions
Common Issues:
- Syntax Errors: Python 2/3 syntax incompatibilities
- Library Availability: Libraries may not support all Python versions
- Package Installation: Packages may not install on certain versions
- Runtime Errors: Applications may fail at runtime with wrong version
Recommendations:
- Verify Compatibility: Check application and library compatibility
- Test Dependencies: Test all Python dependencies
- Use Virtual Environments: Isolate Python environments
- Document Requirements: Keep track of Python version requirements
Node.js Version Changes
Node.js Version Compatibility:
- NPM Compatibility: NPM versions are tied to Node.js versions
- Module Compatibility: Node modules may require specific Node.js versions
- API Changes: Node.js APIs change between versions
- Performance: Different versions have different performance characteristics
Common Issues:
- Module Installation: npm packages may not install on certain versions
- Runtime Errors: Applications may fail with incompatible Node.js versions
- Feature Availability: Features may be added or removed
- Breaking Changes: Major version updates introduce breaking changes
Recommendations:
- Check Node Version: Verify required Node.js version for applications
- Test npm Packages: Ensure all npm packages are compatible
- Use Version Managers: Consider using nvm or similar tools
- Review Changelog: Check Node.js changelog for breaking changes
Restricted Version Changes
Support-Required Version Changes
Due to system criticality, some version changes are blocked from KloudBean side and are only allowed upon request. You have to reach out to support to get this allowed.
What This Means:
- Protected Versions: Some version changes are restricted for system safety
- Support Approval: Requires approval from KloudBean support team
- Safety Measure: Prevents potentially dangerous version changes
- Managed System: KloudBean manages critical system components
Why Restrictions Exist:
- System Stability: Protect server stability and functionality
- Critical Components: Some components are too critical to change freely
- Risk Management: Reduce risk of system breakage
- Managed Responsibility: KloudBean has responsibility to keep system up
How to Request:
- Contact Support: Reach out to KloudBean support via chat or email
- Explain Need: Explain why you need the version change
- Provide Details: Provide package details and target version
- Wait for Approval: Support will review and approve if safe
What Support Will Do:
- Risk Assessment: Evaluate risks of the version change
- Compatibility Check: Verify compatibility with system
- Safe Implementation: Implement change safely if approved
- Monitor Results: Monitor system after change
Installing Additional Packages
Requesting Packages from Support
Apart from this, if you need any other packages on your server, you have to ask KloudBean support team over chat or email, with the package details and need.
Why This Restriction:
- System Safety: KloudBean does not allow you to do it directly because it could result in system breakage
- Managed System: System is managed, so KloudBean has responsibility to keep it up
- Risk Prevention: Prevents installation of packages that could break the system
- Quality Control: Ensures only safe, tested packages are installed
What Happens When You Request:
-
Contact Support: Reach out to KloudBean support team via:
- Live Chat: Available in KloudBean dashboard
- Email: Send email with package details
-
Provide Package Details: Include:
- Package Name: Exact name of the package
- Package Version: Desired version (if specific)
- Purpose: Why you need this package
- Use Case: How you plan to use it
-
Support Review: KloudBean team will:
- Carefully Review: Review those packages and its risks
- Risk Assessment: Evaluate potential risks to system
- Compatibility Check: Verify compatibility with server stack
- Safety Evaluation: Determine if it's safe to proceed
-
Implementation: If approved:
- Safe Installation: KloudBean team will install it safely
- Configuration: Configure package if needed
- Testing: Test to ensure it works correctly
- Notification: Inform you when installation is complete
-
If Not Approved:
- Explanation: Support will explain why it cannot be installed
- Alternatives: May suggest alternative solutions
- Risk Explanation: Explain the risks involved
Benefits of This Approach:
- System Protection: Protects your server from breakage
- Expert Review: Packages reviewed by experts
- Safe Installation: Ensures safe, tested installations
- System Stability: Maintains server stability and performance
- Managed Responsibility: KloudBean takes responsibility for system health
Best Practices
Service Management Best Practices
- Monitor Resource Usage: Regularly check service resource consumption
- Restart When Needed: Restart services after configuration changes
- Don't Stop Critical Services: Never attempt to stop critical services
- Monitor Service Health: Keep an eye on service status and health
Package Management Best Practices
- Test Version Changes: Always test version changes in staging first
- Backup Before Changes: Create backups before making package changes
- Read Documentation: Review package documentation before changes
- Contact Support: Reach out to support for restricted changes or new packages
- Document Changes: Keep track of package versions and changes
Version Management
- Understand Dependencies: Know what depends on packages before changing
- Gradual Updates: Update packages gradually, not all at once
- Monitor After Changes: Watch applications closely after version changes
- Have Rollback Plan: Know how to rollback if issues occur
Troubleshooting
Service Issues
Service Won't Start:
- Check service logs for errors
- Verify configuration files
- Check resource availability
- Contact support if critical service
High Resource Usage:
- Identify which service is consuming resources
- Review service configuration
- Consider optimizing service settings
- Contact support for assistance
Package Issues
Version Change Problems:
- Verify package version compatibility
- Check application logs for errors
- Review dependency conflicts
- Contact support for help
Package Installation Requests:
- Provide complete package details
- Explain use case clearly
- Be patient for support review
- Follow support recommendations
Next Steps
After managing server packages and services:
- Learn about Monitoring Server Health to track resource usage
- Explore Managing Server Backups to protect your server data
- Review Updating Server Stack Settings for configuration options