Managing Server Backups
Learn how to manage server-level backups on KloudBean. KloudBean makes it easy to protect your applications and data with automated backups, ensuring quick recovery from disasters, data loss, or configuration errors.
Overview
Server backups are usually a bit confusing. Your whole server is not backed up - basically, all the applications on your server get backups. By default, KloudBean enables server-level backup, which means all your applications are backed up automatically.
Understanding Server Backups
What Gets Backed Up:
- All Applications: Every application deployed on your server
- Application Data: Files, databases, and configurations for each application
- Application Settings: Configuration files and settings
- Not the Entire Server: The operating system and server infrastructure are not backed up
Why This Approach:
- Focused Protection: Protects what matters most - your applications and data
- Efficient: More efficient than backing up the entire server
- Faster Restoration: Faster restore times for applications
- Cost-Effective: More cost-effective than full server backups
Importance of Backups
Data Protection:
- Prevent Data Loss: Protect against accidental deletion, corruption, or data loss
- Disaster Recovery: Recover quickly from server failures or disasters
- Configuration Errors: Restore previous working configurations
- Security Incidents: Recover from security breaches or malware attacks
Business Continuity:
- Minimize Downtime: Quick restoration reduces business impact
- Peace of Mind: Know your data is protected
- Compliance: Meet data retention and backup requirements
- Version Control: Access previous versions of your applications
KloudBean Makes It Easy:
- Automated Backups: Set it and forget it - backups happen automatically
- Simple Configuration: Easy-to-use interface for backup settings
- One-Click Restore: Restore applications with a single click
- Comprehensive Protection: All applications backed up by default
- Flexible Options: Customize backup schedule and retention to your needs
Prerequisites
- An active KloudBean server
- Access to server administration settings
- Sufficient disk space for backups (if using onsite backups)
Accessing Backup Settings
Step 1: Navigate to Manage Backups
In order to access server backup settings:
- Log in to your KloudBean dashboard
- Navigate to Server Administration: Open the server administration page for your desired server
- Go to "Manage Backups" Tab: Click on the "Manage Backups" tab in the server settings menu
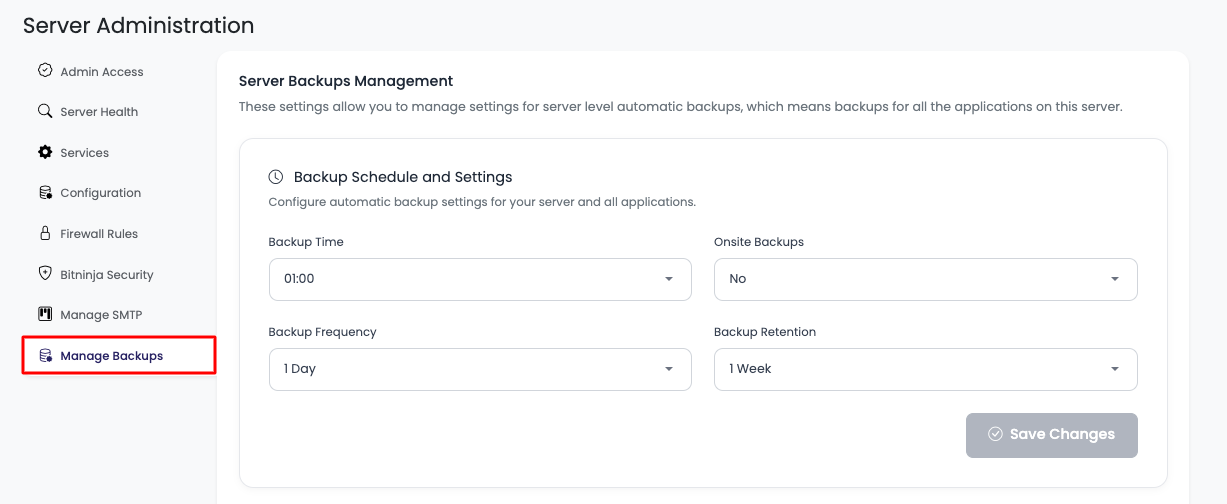
On this tab, you will see backups current/default settings.
Configuring Backup Settings
For your apps backups, you can control these settings:
Backup Time
Default Value: 1:00 AM
What It Is: The time of day when automatic backups are initiated.
Why It Matters:
- Low Traffic Periods: Schedule backups during times when your server has low traffic
- Minimal Impact: Reduces impact on user experience during backup process
- Resource Availability: Ensures server resources are available for backup operations
- Consistency: Regular backup times make it easier to track and manage backups
When to Adjust:
- Server Load Patterns: Adjust based on when your server experiences lowest traffic
- Time Zone Considerations: Consider your primary user base's time zone
- Application Usage: Schedule when applications are least used
- Peak Hours: Avoid scheduling during peak business hours
Best Practices:
- Off-Peak Hours: Schedule during off-peak hours (typically 1:00 AM - 4:00 AM)
- Weekend Consideration: Consider weekend times if weekdays are busier
- Global Audience: If serving global audience, choose time that affects fewest users
- Test Impact: Monitor server performance during backup times
Backup Frequency
Default Value: Once a day
Available Options: You can change it from 6 hours to 7 days
What It Is: How often automatic backups are created for your applications.
Why It Matters:
- Data Freshness: More frequent backups mean less data loss in case of failure
- Recovery Point Objective (RPO): Determines how much data you can afford to lose
- Storage Costs: More frequent backups consume more storage space
- Server Impact: More frequent backups may impact server performance
Available Frequencies:
- Every 6 Hours: Maximum frequency for critical applications
- Every 12 Hours: Good balance for important applications
- Once a Day (Default): Suitable for most applications
- Every 2 Days: For less critical applications
- Every 3 Days: For development or staging environments
- Once a Week: For non-critical applications
- Every 7 Days: Maximum interval
When to Choose Each Frequency:
Every 6 Hours:
- Critical Applications: E-commerce, financial, healthcare applications
- High Transaction Volume: Applications with frequent data changes
- Low RPO Requirements: When you can't afford to lose more than 6 hours of data
- Important Consideration: Higher storage costs and server impact
Once a Day (Default):
- Most Applications: Suitable for majority of applications
- Balanced Approach: Good balance between protection and cost
- Standard Practice: Industry standard for most web applications
- Recommended: Best starting point for most users
Less Frequent (2-7 Days):
- Development Servers: Non-production environments
- Low-Change Applications: Applications with infrequent updates
- Cost Optimization: When storage costs are a concern
- Staging Environments: Testing and staging servers
Important Warning: Be careful with selection - choosing too infrequent backups means more data loss in case of failure. Choose based on your application's criticality and data change frequency.
Onsite Backups
Default State: Off by default
What It Is: When enabled, a copy of backup will also be created on your server (in addition to offsite backup).
Why It Matters:
- Quick Access: Faster access to backups stored locally on server
- Download Convenience: Useful when you intend to download backups
- Redundancy: Additional copy provides extra protection
- Local Storage: Backups stored on server's disk
When to Enable:
- Frequent Downloads: If you regularly download backups
- Quick Restore: For faster local restore operations
- Additional Safety: For extra backup redundancy
- Development: Useful for development/staging environments
When to Keep Disabled:
- Storage Constraints: If server disk space is limited
- Cost Optimization: To reduce storage costs
- Offsite Only: If offsite backups are sufficient
- Production Servers: When offsite backup is primary protection
Considerations:
- Disk Space: Onsite backups consume server disk space
- Performance Impact: May impact server performance during backup
- Storage Management: Need to manage local backup storage
- Cost: Additional storage may incur costs
Backup Retention
Default Value: 7 days
Available Range: You can keep backups up to 5 weeks
What It Is: Backup retention means how much older backups should be kept before being automatically deleted.
Why It Matters:
- Recovery Window: Determines how far back you can restore
- Storage Management: Controls how much storage is used
- Cost Management: Longer retention = higher storage costs
- Compliance: May need to meet retention requirements
Available Options:
- 7 Days (Default): Keep backups for 1 week
- 14 Days: Keep backups for 2 weeks
- 21 Days: Keep backups for 3 weeks
- 30 Days: Keep backups for 1 month
- 35 Days: Maximum retention (5 weeks)
When to Choose Each Retention Period:
7 Days (Default):
- Most Applications: Suitable for majority of use cases
- Cost-Effective: Lower storage costs
- Standard Practice: Industry standard retention period
- Recommended: Good starting point
14-21 Days:
- Important Applications: Applications with moderate importance
- Compliance Needs: When regulations require longer retention
- Change Management: When you need to track changes over time
- Audit Requirements: For applications requiring audit trails
30-35 Days (5 Weeks):
- Critical Applications: Mission-critical applications
- Compliance Requirements: When regulations require extended retention
- Change History: When you need extended change history
- Important Note: Increasing backup retention will cause more cost
Cost Considerations:
- Storage Costs: Longer retention = more storage used = higher costs
- Cost vs. Protection: Balance between cost and protection needs
- Evaluate Needs: Assess if extended retention is necessary
- Optimize: Choose retention that meets your needs without overpaying
Best Practices:
- Start with Default: Begin with 7 days and adjust as needed
- Assess Requirements: Determine your actual recovery needs
- Monitor Costs: Keep an eye on storage costs
- Review Regularly: Periodically review if retention period is appropriate
Taking On-Demand Backup
Step 2: Initiate On-Demand Backup
You can initiate your server-level backup (backup all apps) anytime on demand.
Scroll a little down where you will see a button to initiate backup.
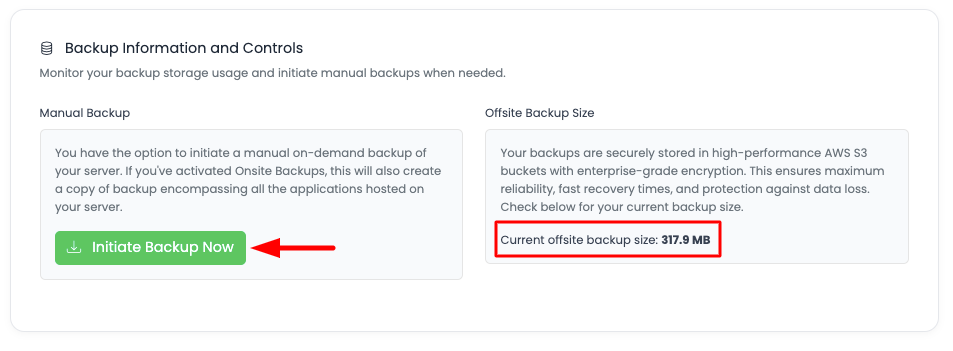
Here you will also see the total current offsite backup size.
Step 3: Confirm Backup Initiation
If you wish to take backup, click on "Initiate Backup Now". It will open a prompt and view the total number of apps with list which will be backed up. This information is helpful.
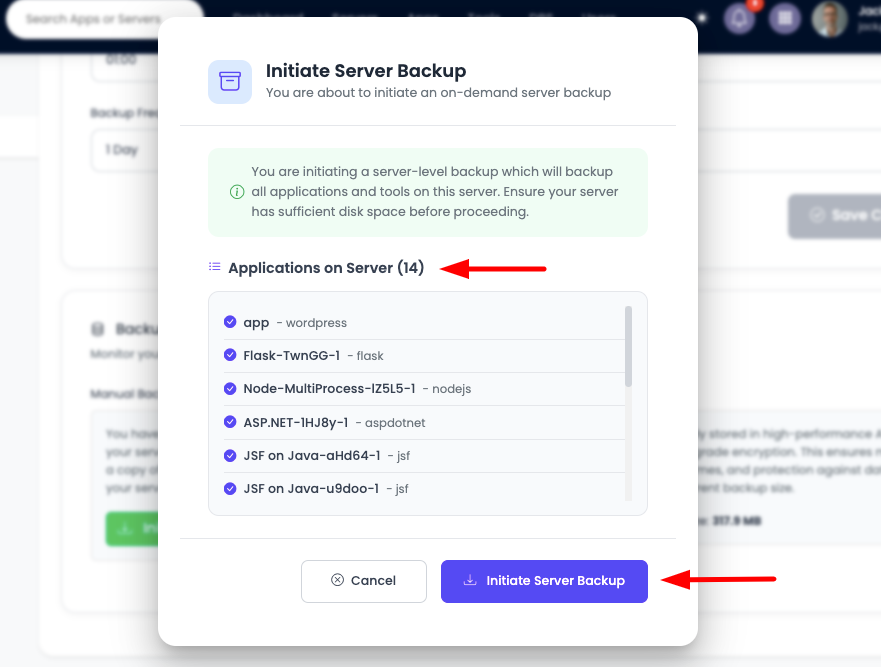
Important Information Displayed:
- Total Applications: Number of applications that will be backed up
- Application List: Detailed list of all applications to be backed up
- Backup Scope: Confirmation that this is a server-level backup
- Warning Message: "You are initiating a server-level backup which will backup all applications and tools on this server. Ensure your server has sufficient disk space before proceeding."
Before Proceeding:
- Check Disk Space: Make sure you have enough space on server to run full backup
- Review Applications: Verify the list of applications is correct
- Consider Timing: Choose a time when server load is manageable
- Plan Accordingly: Be aware that server will be busy during backup
Step 4: Backup Process
What Happens During Backup:
- Server Status: Your server will stay busy during this process
- Web App Accessibility: However, your web apps will still be accessible
- Console Lock: It's just KloudBean console which will be locked for that server until backup is completed
- Background Process: Backup runs in the background
What This Means:
- Users Unaffected: Users can still access your web applications
- Server Resources: Server resources are used for backup operations
- Console Access: You won't be able to make changes via console during backup
- Completion Time: Backup completion time depends on data size
Best Practices:
- Plan Ahead: Initiate backups during low-traffic periods when possible
- Monitor Progress: Check backup status periodically
- Wait for Completion: Don't interrupt the backup process
- Verify Success: Confirm backup completed successfully
Why Backups Are Critical
Protection Against Data Loss
Accidental Deletion:
- Human Error: Protect against accidental file or data deletion
- Configuration Mistakes: Recover from configuration errors
- Update Failures: Restore if updates cause issues
- Quick Recovery: Minimize downtime from mistakes
System Failures:
- Hardware Failures: Recover from server hardware issues
- Software Crashes: Restore after application crashes
- Corruption: Recover from data corruption
- Disaster Recovery: Full recovery from catastrophic failures
Business Continuity
Minimize Downtime:
- Quick Restoration: Restore applications quickly to minimize business impact
- Service Availability: Maintain service availability for users
- Revenue Protection: Protect revenue by reducing downtime
- Reputation: Maintain business reputation with reliable service
Compliance and Legal:
- Data Retention: Meet legal data retention requirements
- Audit Trails: Maintain audit trails for compliance
- Regulatory Compliance: Meet industry-specific regulations
- Legal Protection: Protect against legal issues with proper backups
Peace of Mind
Confidence:
- Risk Mitigation: Know your data is protected
- Stress Reduction: Reduce stress about potential data loss
- Focus on Business: Focus on business instead of worrying about backups
- Reliable Protection: Trust in reliable backup system
How KloudBean Makes Backups Easy
Automated Protection
Set It and Forget It:
- Default Enabled: Server-level backups enabled by default
- Automatic Execution: Backups run automatically on schedule
- No Manual Intervention: No need to remember to backup
- Consistent Protection: Regular, consistent backup protection
Simple Configuration
User-Friendly Interface:
- Easy Settings: Simple, intuitive backup settings
- Clear Options: Clear explanation of each setting
- Flexible Scheduling: Flexible backup scheduling options
- One-Click Changes: Easy to modify backup settings
Comprehensive Coverage
All Applications Protected:
- Server-Level: All applications backed up automatically
- Complete Protection: Nothing is missed
- Consistent: Same protection for all applications
- Reliable: Dependable backup coverage
Easy Restoration
Quick Recovery:
- Simple Restore: Easy restore process when needed
- Selective Restore: Restore specific applications if needed
- Fast Recovery: Quick recovery times
- Reliable Restoration: Dependable restore process
Cost-Effective
Optimized Storage:
- Efficient Backups: Efficient backup storage
- Flexible Retention: Choose retention that fits your budget
- Cost Control: Control costs with flexible options
- Value: Great value for comprehensive protection
Backup Best Practices
Regular Monitoring
- Check Backup Status: Regularly verify backups are completing successfully
- Review Backup Logs: Periodically review backup logs for issues
- Test Restores: Periodically test restore process to ensure it works
- Monitor Storage: Keep an eye on backup storage usage
Optimal Configuration
- Right Frequency: Choose backup frequency based on application criticality
- Appropriate Retention: Set retention based on actual needs
- Optimal Timing: Schedule backups during low-traffic periods
- Balance Cost: Balance protection needs with costs
Storage Management
- Monitor Space: Regularly check available disk space
- Clean Up: Remove old backups when no longer needed
- Optimize Settings: Adjust settings to optimize storage usage
- Plan for Growth: Plan backup storage for application growth
Troubleshooting
Backup Failures
Common Issues:
- Insufficient Disk Space: Ensure server has enough disk space
- Server Resources: Check if server has adequate resources
- Network Issues: Verify network connectivity for offsite backups
- Permission Problems: Check file permissions
Solutions:
- Free Up Space: Clean up disk space if needed
- Check Logs: Review backup logs for specific errors
- Contact Support: Reach out to KloudBean support for assistance
- Retry Backup: Try initiating backup again after resolving issues
Performance Issues
During Backup:
- Expected Behavior: Some performance impact is normal during backup
- Timing: Schedule backups during low-traffic periods
- Monitor Resources: Monitor server resources during backup
- Patience: Allow backup to complete without interruption
Next Steps
After configuring server backups:
- Learn about Managing Server Packages and Services to manage server components
- Explore Monitoring Server Health to track server performance
- Review Server SSH Access Control for additional security