Monitoring Load Balancer Health
Learn how to monitor your load balancer's health and resource utilization on KloudBean. Keeping an eye on resource utilization is crucial to avoid resource congestion issues or production downtime.
Overview
KloudBean provides a user-friendly UI to view your load balancer health and utilization of resources. It is important to keep an eye on resource utilization in order to avoid any resource congestion issues or production downtime. Regular monitoring helps you identify potential issues before they impact your applications and allows you to make informed decisions about scaling and optimization.
KloudBean's Optimized Infrastructure
KloudBean provides load balancers that are already best optimized, and you are having high-performance hardware. Complete stack components along with kernel parameters are optimized and tuned to give the best performance. However, each resource still has its limitations. If you are seeing resource consumption at a critical level, then ask KloudBean to scale up. If you see resources in a warning state, then consider optimizing your application code or plan to do some optimization, or plan to scale up in the near future.
Types of Monitoring
KloudBean provides two types of monitoring:
1. Load Balancer Health Status Page
Navigate to load balancer administration → "Server Health" to view real-time load balancer health metrics and resource utilization. This provides a comprehensive visual dashboard of all critical load balancer components.
2. Email Alerts
KloudBean sends email alerts when the load balancer reaches critical limits. These alerts are automatically sent to your registered email address, ensuring you're immediately notified of any critical resource issues.
Accessing Load Balancer Health Monitoring
Step 1: Navigate to Load Balancer Health
To view your load balancer health:
- Log in to your KloudBean dashboard
- Navigate to Load Balancer Administration: Open the load balancer administration page for your desired Flexible Load Balancer
- Go to "Server Health": Click on "Server Health" in the load balancer settings menu
Step 2: View Complete Load Balancer Health Overview
This section provides utilization stats for all critical components. Here is the complete view of load balancer health:
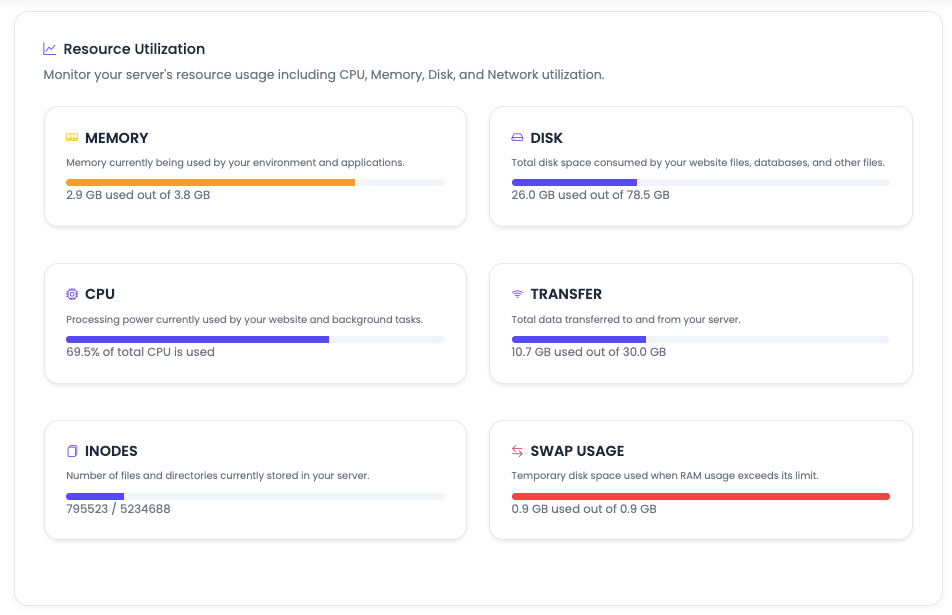
Monitored Resources
KloudBean monitors all these resources and displays their utilization:
- MEMORY: RAM usage and availability
- DISK: Storage space and disk I/O
- CPU: Processor utilization and load
- DATA TRANSFERRED: Network bandwidth usage
- INODES: File system inode usage
- SWAP MEMORY: Virtual memory usage
Understanding Color Indicators
KloudBean uses color coding to quickly indicate resource status:
- Blue: Resources are in good condition, not much used. This indicates healthy resource levels with plenty of capacity available.
- Yellow: Warning state. Resources are approaching their limits, and you should monitor closely or consider optimization or scaling.
- Red: Critical condition. Resources are at or near their maximum capacity, and immediate action is required to prevent service disruption.
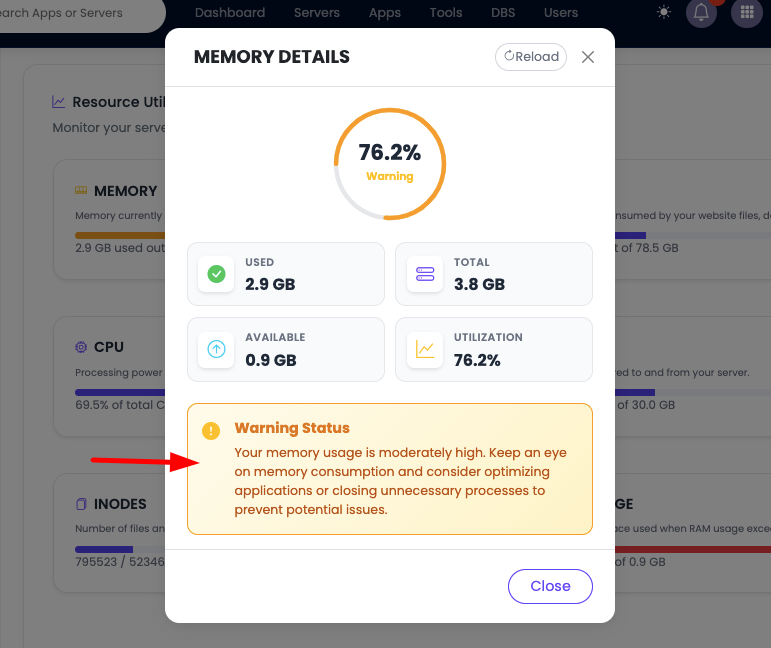
Viewing Detailed Resource Information
To view more detailed information about a particular resource:
- Click on the Resource: Click on the specific resource card or section you want to examine
- View Detailed Metrics: You'll see expanded information.
Understanding Each Resource
Memory (RAM)
What It Is: Random Access Memory (RAM) is the primary storage for active data and running processes. For load balancers, RAM is critical for handling connection pools, SSL/TLS operations, and traffic routing.
Why Monitor Memory for Load Balancers:
- Connection Handling: Load balancers need memory to maintain active connections
- SSL/TLS Processing: SSL certificate operations consume memory
- Traffic Routing: Memory is used for routing tables and session information
- Performance: Insufficient memory causes load balancer slowdowns and connection drops
- High Availability: Memory affects the ability to handle traffic spikes
What to Watch For:
- Memory usage consistently above 80% indicates you may need more RAM
- Rapid memory growth may indicate connection leaks or traffic spikes
- High swap usage means you're running out of physical RAM
- Memory spikes during traffic surges
Recommendation: If you observe high memory utilization consistently, contact KloudBean to scale up your load balancer's RAM. For warning levels, consider optimizing your application traffic patterns or plan for scaling in the near future.
Disk Storage
What It Is: Disk storage is where all your load balancer configuration files, SSL certificates, logs, and temporary data are stored. Unlike RAM, disk storage persists even when the load balancer is powered off.
Why Monitor Disk for Load Balancers:
- SSL Certificate Storage: SSL certificates and keys are stored on disk
- Configuration Files: Load balancer configuration files require disk space
- Log Management: Access logs and error logs can consume significant disk space
- Performance: Full disks significantly slow down SSL operations and log writing
- Certificate Management: Adequate disk space is needed for certificate storage and updates
What to Watch For:
- Disk usage above 80% requires attention
- Rapid disk space consumption may indicate log file growth
- Low disk space can prevent SSL certificate updates
- Disk I/O performance degradation as disk fills up
Recommendation: If disk utilization reaches critical levels, contact KloudBean to scale up your storage. For warning states, consider cleaning up old logs, archiving old access logs, or planning for storage expansion.
CPU (Central Processing Unit)
What It Is: The CPU is the brain of your load balancer, executing instructions for traffic routing, SSL/TLS encryption/decryption, health checks, and load balancing algorithms.
Why Monitor CPU for Load Balancers:
- Traffic Routing: CPU processes all incoming requests and routes them to backend servers
- SSL/TLS Processing: SSL encryption and decryption are CPU-intensive operations
- Health Checks: CPU executes health check requests to backend servers
- Load Balancing Algorithms: CPU calculates routing decisions based on algorithms
- Response Times: CPU bottlenecks cause slow response times for users
What to Watch For:
- Sustained CPU usage above 95% indicates you need more processing power
- CPU spikes during traffic surges may indicate need for scaling
- High CPU load averages suggest the load balancer is overloaded
- CPU wait times indicate I/O bottlenecks or backend server issues
Recommendation: If CPU utilization consistently reaches critical levels, contact KloudBean to scale up your load balancer's CPU resources. For warning states, consider optimizing SSL/TLS settings, reducing health check frequency, or planning for scaling.
Data Transferred (Network Bandwidth)
What It Is: Data transferred represents the amount of network traffic (incoming and outgoing) your load balancer handles. This includes all web requests, SSL/TLS traffic, health checks, and traffic routed to backend servers.
Why Monitor Data Transfer for Load Balancers:
- Bandwidth Limits: Exceeding bandwidth limits can result in additional charges or throttling
- Traffic Distribution: Understanding traffic helps with capacity planning
- DDoS Detection: Unusual traffic spikes may indicate attacks
- Performance: High network usage can slow down load balancer responses
- Cost Management: Monitoring helps control bandwidth costs
What to Watch For:
- Sudden spikes in data transfer may indicate traffic anomalies or attacks
- Consistently high transfer rates may require bandwidth upgrades
- Incoming vs outgoing traffic patterns
- Peak usage times and traffic trends
Recommendation: If data transfer consistently reaches limits, contact KloudBean to upgrade your bandwidth plan. Monitor traffic patterns to identify optimization opportunities like CDN usage or caching strategies.
Inodes
What It Is: Inodes are data structures that store information about files and directories on your file system. Each file, directory, or symbolic link uses one inode.
Why Monitor Inodes for Load Balancers:
- File System Limits: Running out of inodes prevents creating new files, even if disk space is available
- Log File Management: Many log files can exhaust inodes quickly
- SSL Certificate Files: Certificate files and keys consume inodes
- System Operations: Low inodes can prevent system updates and operations
- Configuration Files: Load balancer configuration changes require inodes
What to Watch For:
- Inode usage above 80% requires attention
- Rapid inode consumption may indicate excessive log file creation
- Many small files (like log files, cache files) consume inodes quickly
- Inode exhaustion can occur even with plenty of disk space available
Recommendation: If inode usage reaches critical levels, contact KloudBean for assistance. Consider cleaning up unnecessary files, optimizing log rotation, or planning for inode capacity increases.
Swap Memory
What It Is: Swap memory is disk space used as virtual memory when physical RAM is full. The system moves less-used data from RAM to swap to free up RAM for active processes.
Why Monitor Swap for Load Balancers:
- Performance Indicator: High swap usage indicates insufficient RAM
- Performance Degradation: Using swap is much slower than RAM, causing significant performance issues
- Connection Handling: Swap usage affects the load balancer's ability to handle connections
- SSL/TLS Performance: SSL operations become very slow when swap is heavily used
- Traffic Routing: Swap usage can cause delays in traffic routing decisions
What to Watch For:
- Any significant swap usage suggests you need more RAM
- High swap activity (swapping in/out) indicates memory pressure
- Swap usage combined with high memory usage confirms RAM shortage
- Performance degradation correlates with swap usage
Recommendation: If swap memory is being used consistently, contact KloudBean to increase your load balancer's RAM. Swap usage is a clear indicator that your load balancer needs more memory resources.
Load Balancer-Specific Monitoring
Traffic Distribution Metrics
Monitor how traffic is distributed across backend servers:
- Requests per Second: Current request rate through the load balancer
- Active Connections: Number of active connections being handled
- Backend Server Health: Health status of each backend server
- Traffic Distribution: How traffic is distributed among backend servers
- Response Times: Average response times from backend servers
SSL/TLS Metrics
Monitor SSL/TLS performance:
- SSL Handshakes: Number of SSL handshakes per second
- SSL Certificate Status: Status of SSL certificates
- HTTPS Traffic: Amount of HTTPS vs HTTP traffic
- SSL Errors: SSL/TLS error rates
- Certificate Expiration: Days until certificate expiration
Health Check Status
Monitor backend server health:
- Healthy Servers: Number of healthy backend servers
- Unhealthy Servers: Number of servers failing health checks
- Health Check Response Times: Time taken for health checks
- Health Check Failures: Frequency of health check failures
- Automatic Failover: Servers automatically removed from pool
Monitoring Via Email Alerts
KloudBean sends alerts if any resource utilization crosses the limit. Alerts are sent automatically to your registered email address.
Alert Thresholds
By default, these thresholds are set to trigger email alerts:
- CPU_THRESHOLD=95%: Alert when CPU usage exceeds 95%
- MEM_THRESHOLD=85%: Alert when memory usage exceeds 85%
- DISK_THRESHOLD=80%: Alert when disk usage exceeds 80%
How Email Alerts Work
- Automatic Monitoring: KloudBean continuously monitors all load balancer resources
- Threshold Detection: When a resource exceeds its threshold, an alert is triggered
- Email Notification: An email is automatically sent to your registered email address
- Alert Details: The email includes:
- Which resource exceeded the threshold
- Current utilization percentage
- Recommended actions
- Load balancer information
Responding to Alerts
Critical Alerts (Red):
- Immediate Action: Contact KloudBean support to scale up resources
- Investigation: Check what's causing the high utilization
- Traffic Management: Consider temporarily reducing traffic or optimizing routing
Warning Alerts (Yellow):
- Monitor Closely: Keep an eye on the resource usage
- Optimization: Consider optimizing your load balancer configuration
- Planning: Plan for scaling in the near future
- Preventive Action: Take action before it becomes critical
Best Practices for Load Balancer Health Monitoring
Regular Monitoring
- Daily Checks: Review load balancer health dashboard daily
- Weekly Reviews: Analyze weekly trends and patterns
- Monthly Analysis: Review monthly reports for capacity planning
- Alert Response: Respond promptly to email alerts
Proactive Management
- Address Warnings Early: Don't wait for critical alerts
- Optimize Before Scaling: Try optimization before scaling up
- Monitor Trends: Watch for gradual increases in resource usage
- Plan Ahead: Scale resources before reaching critical levels
Optimization vs Scaling
When to Optimize:
- Resources are in warning state (yellow)
- You can identify optimization opportunities in configuration
- Performance issues are configuration-related, not resource-related
- You want to maximize current resource efficiency
When to Scale Up:
- Resources consistently reach critical levels (red)
- Optimization has been attempted but resources are still insufficient
- Traffic or workload has genuinely increased
- You need immediate capacity increase
Resource Planning
- Baseline Metrics: Establish normal baseline metrics for your load balancer
- Growth Projections: Plan for future growth based on trends
- Peak Times: Identify peak usage times and plan accordingly
- Capacity Planning: Plan scaling before resources become critical
Troubleshooting Resource Issues
High Memory Usage
- Identify Processes: Check which processes are using the most memory
- Connection Leaks: Look for connection pool issues
- Traffic Spikes: Identify unusual traffic patterns
- Scale Up: Contact KloudBean to increase RAM if optimization isn't sufficient
High CPU Usage
- Identify CPU-Intensive Operations: Find processes consuming CPU resources
- SSL/TLS Optimization: Optimize SSL/TLS settings
- Health Check Frequency: Reduce health check frequency if needed
- Scale Up: Contact KloudBean to increase CPU resources if needed
High Disk Usage
- Identify Large Files: Find files consuming disk space
- Clean Up Logs: Remove unnecessary log files
- Archive Old Data: Move old logs to archival storage
- Scale Up: Contact KloudBean to increase disk storage
High Inode Usage
- Find File Sources: Identify directories with many small files
- Clean Up: Remove unnecessary files and directories
- Optimize Log Rotation: Review log rotation settings
- Contact Support: Reach out to KloudBean for inode capacity solutions
KloudBean's Optimized Infrastructure
Pre-Optimized Load Balancers
KloudBean provides load balancers that are already best optimized with:
- High-Performance Hardware: Latest generation processors and fast storage
- Optimized Stack Components: All software components are optimized for performance
- Tuned Kernel Parameters: System kernel is tuned for optimal performance
- Best Practices Applied: Industry best practices implemented by default
Performance Benefits
- Maximum Efficiency: Get the best performance from your resources
- Reduced Overhead: Optimized systems have lower overhead
- Better Resource Utilization: More efficient use of available resources
- Proven Configurations: Tested and proven optimal configurations
When Resources Still Have Limits
Despite optimization, each resource still has its limitations:
- Physical Constraints: Hardware has physical limits
- Traffic Growth: Applications and traffic grow over time
- Resource Exhaustion: Even optimized systems can run out of resources
- Scaling Needs: Growth requires additional resources
Making Scaling Decisions
If you see resource consumption at a critical level (Red):
- Immediate Action: Contact KloudBean to scale up immediately
- Prevent Downtime: Scaling prevents service disruption
- Quick Resolution: KloudBean can help scale resources quickly
If you see resources in warning state (Yellow):
- Optimize First: Consider optimizing your load balancer configuration
- Plan Optimization: Review configuration for efficiency improvements
- Plan Scaling: Plan to scale up in the near future
- Monitor Closely: Keep monitoring to prevent critical state
Next Steps
After monitoring your load balancer health:
- Learn about Updating Application Pool to manage backend servers
- Explore Adding SSL Certificates to secure your load balancer
- Review Load Balancer FAQs for common questions