Configure Backup Settings
Learn how to configure and manage database backup settings on KloudBean. KloudBean provides a very straightforward and efficient way to manage your database backups.
Overview
KloudBean provides a very straightforward and efficient way to manage your database backups.
Key Features:
- Offsite Storage: Backups are stored offsite for security and redundancy
- Easy Restoration: You can restore database anytime to any available backups
- Restore to New Instance: You can restore database to a new instance (for this option you should have premium support package enabled)
- Automated Backups: Automatic backup scheduling and management
- Configurable Settings: Customize backup time, frequency, and retention
Why Backups Matter:
- Data Protection: Protect your data from loss, corruption, or accidental deletion
- Disaster Recovery: Recover from system failures or disasters
- Point-in-Time Recovery: Restore to specific points in time
- Compliance: Meet data retention and compliance requirements
- Peace of Mind: Know your data is safe and recoverable
Prerequisites
- An active database instance on KloudBean
- Admin access to your KloudBean account
- Understanding of your backup requirements
- (For restore to new instance) Premium support package enabled
Viewing Backup Settings
Step 1: Navigate to Backup Settings
In order to update database backup settings, navigate to Database Administration → "Backups" tab.
Steps:
- Log in to your KloudBean dashboard
- Navigate to Databases: Go to the Databases section
- Select Your Database: Click on your database instance
- Go to Backups: Navigate to "Backups" tab in database administration
Step 2: View Current Backup Settings
On this tab you will be able to see database current settings.
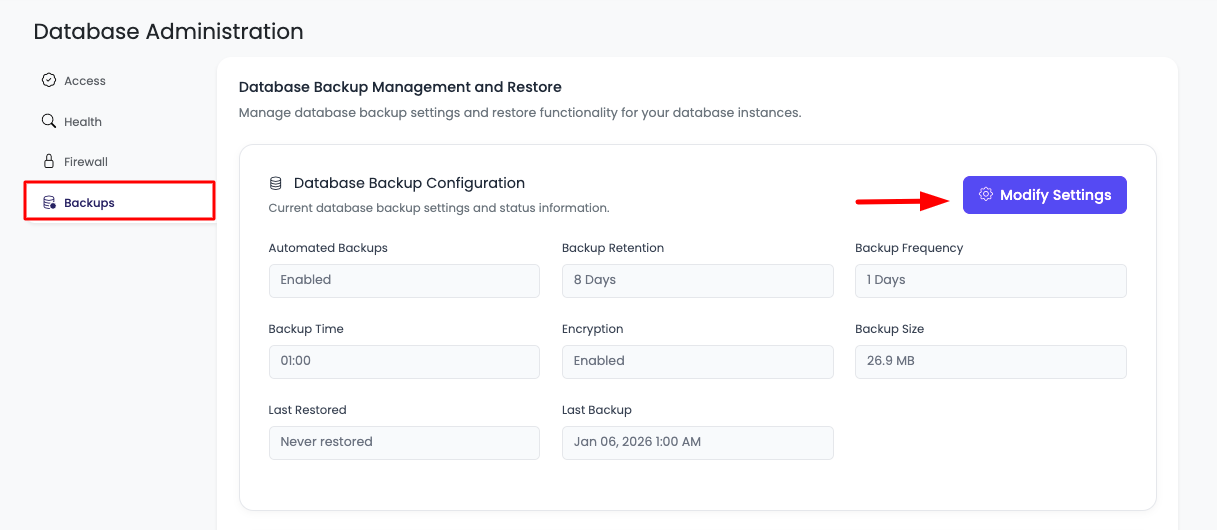
Information Displayed:
- Backup Status: Whether backups are enabled or disabled
- Current Backup Time: Scheduled backup time
- Backup Frequency: How often backups are taken
- Backup Retention: How long backups are kept
- Backup Encryption: Encryption status (always enabled)
- Recent Backups: List of recent backups
- Backup Storage: Storage usage information
Updating Backup Settings
Step 1: Access Modify Settings
In order to update settings, click on "Modify Settings" button.
It will open a prompt, asking to adjust new settings.
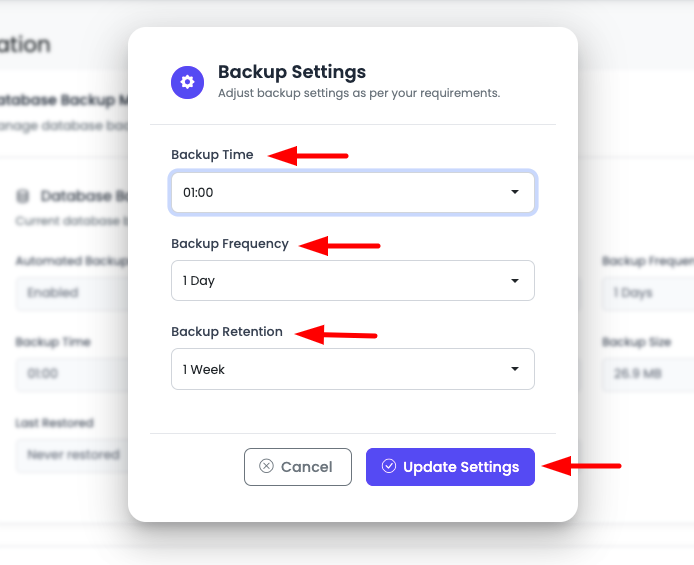
Step 2: Configure Backup Settings
You can update these settings:
Backup Time
Default: 01:00 (1:00 AM)
What It Is: The time of day when automated backups are taken.
Configuration:
- Time Format: 24-hour format (00:00 to 23:59)
- Default Time: 01:00 (1:00 AM)
- Time Zone: Uses server timezone
- Selection: Choose from dropdown or enter custom time
Why Backup Time Matters:
- Low Traffic Period: Backups should run during low-traffic periods
- Minimal Impact: Reduces impact on database performance
- Consistent Schedule: Predictable backup schedule
- Resource Availability: Ensures resources are available for backup
Best Practices:
- Off-Peak Hours: Schedule during off-peak hours (typically 1-4 AM)
- Business Hours: Avoid backup times during business hours
- Consistent Time: Use the same time daily for consistency
- Consider Timezone: Consider your application's timezone and user base
Recommendation: Keep the default time (01:00) unless you have specific requirements. This time is typically when database traffic is lowest.
Backup Frequency
Default: 1 Days (Daily backups)
What It Is: How often automated backups are taken.
Configuration Options:
- 1 Day: Daily backups (recommended for most cases)
- 2 Days: Every 2 days
- 3 Days: Every 3 days
- 7 Days: Weekly backups
- Custom: Other frequency options
Why Backup Frequency Matters:
- Data Loss Risk: More frequent backups reduce potential data loss
- Recovery Point: Determines how far back you can recover
- Storage Usage: More frequent backups use more storage
- Performance Impact: More frequent backups may impact performance
Choosing the Right Frequency:
- Daily (Recommended): Best balance of protection and storage
- Multiple Times Daily: For critical databases with high transaction volume
- Weekly: For less critical databases or development environments
- Custom: Based on your specific requirements
Considerations:
- Data Criticality: How critical is your data?
- Change Rate: How often does your data change?
- Storage Costs: More frequent backups use more storage
- Recovery Needs: How far back do you need to recover?
Recommendation: Use daily backups (1 Day) for production databases. This provides good protection with reasonable storage usage.
Backup Retention
Default: 8 Days
What It Is: How long backups are kept before being automatically deleted.
Configuration:
- Retention Period: Number of days to keep backups
- Default: 8 days
- Range: Typically 1-90 days (varies by plan)
- Automatic Cleanup: Old backups are automatically deleted
Why Backup Retention Matters:
- Recovery Window: Determines how far back you can recover
- Storage Management: Longer retention uses more storage
- Compliance: May need to meet retention requirements
- Cost: Longer retention may increase storage costs
Choosing the Right Retention:
- Short Retention (1-7 days): For development or non-critical databases
- Medium Retention (8-14 days): Good balance for most production databases
- Long Retention (15-30 days): For critical databases or compliance requirements
- Extended Retention (30+ days): For compliance or regulatory requirements
Considerations:
- Recovery Needs: How far back might you need to recover?
- Storage Capacity: Available storage for backups
- Compliance Requirements: Any regulatory retention requirements?
- Cost: Storage costs for longer retention
Recommendation: 8 days (default) is a good starting point. Adjust based on your recovery needs and storage capacity.
Retention Examples:
- Daily Backups with 8-Day Retention: Keeps last 8 daily backups
- Daily Backups with 30-Day Retention: Keeps last 30 daily backups
- Weekly Backups with 4-Week Retention: Keeps last 4 weekly backups
Backup Encryption
Status: Backup encryption is by default enabled and you cannot change it.
What It Is: All backups are automatically encrypted for security.
Encryption Details:
- Always Enabled: Encryption cannot be disabled
- Automatic: Encryption happens automatically during backup
- Strong Encryption: Uses industry-standard encryption algorithms
- No Configuration Needed: No additional setup required
Why Encryption Matters:
- Data Security: Protects backup data from unauthorized access
- Compliance: Meets security and compliance requirements
- Offsite Storage: Important for offsite backup storage
- Data Protection: Protects sensitive data in backups
Benefits:
- Secure Storage: Backups are secure even if storage is compromised
- Compliance: Meets data protection regulations
- Peace of Mind: Know your backups are protected
- No Action Required: Automatic encryption, no configuration needed
Step 3: Save Settings
Once updated, click "Save" button to update them.
After Saving:
- Settings Applied: New settings are immediately applied
- Next Backup: Next backup will use the new settings
- Confirmation: You'll see confirmation that settings are saved
- Verification: Verify settings are correct after saving
Understanding Backup Features
Offsite Storage
Backups are stored offsite.
What This Means:
- Separate Location: Backups are stored in a different location from your database
- Disaster Protection: Protects against disasters affecting your primary database
- Redundancy: Additional layer of data protection
- Security: Offsite storage provides additional security
Benefits:
- Disaster Recovery: Can recover even if primary location is affected
- Data Safety: Multiple copies of your data in different locations
- Reliability: Redundant storage ensures availability
- Security: Offsite storage adds security layer
Restore Capabilities
You can restore database anytime to any available backups.
Restore Options:
- Point-in-Time Restore: Restore to any available backup point
- Latest Backup: Restore to the most recent backup
- Specific Backup: Choose a specific backup to restore to
- Same Instance: Restore to the same database instance
- New Instance: Restore to a new database instance (premium support required)
Restore to New Instance:
You can restore database to a new instance (for this option you should have premium support package enabled).
What This Means:
- New Database: Create a new database instance from backup
- Premium Support: Requires premium support package
- Use Cases:
- Testing restores
- Creating staging environments
- Disaster recovery to new infrastructure
- Database migration
Benefits:
- Testing: Test restores without affecting production
- Staging: Create staging environments from production backups
- Migration: Migrate to new infrastructure
- Disaster Recovery: Recover to new infrastructure if needed
How to Restore:
- Select Backup: Choose the backup you want to restore from
- Choose Option: Select restore to same instance or new instance
- Configure: Configure restore settings if needed
- Initiate Restore: Start the restore process
- Monitor: Monitor restore progress
Backup Settings Summary
Default Settings
Default Configuration:
- Backup Time: 01:00 (1:00 AM)
- Backup Frequency: 1 Day (Daily)
- Backup Retention: 8 Days
- Backup Encryption: Enabled (cannot be changed)
Recommended Settings
For Production Databases:
- Backup Time: 01:00 - 04:00 (off-peak hours)
- Backup Frequency: 1 Day (Daily)
- Backup Retention: 8-14 Days
- Backup Encryption: Enabled (automatic)
For Development Databases:
- Backup Time: Any off-peak time
- Backup Frequency: 1-3 Days
- Backup Retention: 3-7 Days
- Backup Encryption: Enabled (automatic)
For Critical Databases:
- Backup Time: 01:00 (lowest traffic)
- Backup Frequency: 1 Day (or multiple times daily if available)
- Backup Retention: 14-30 Days
- Backup Encryption: Enabled (automatic)
Best Practices
Backup Scheduling
- Off-Peak Hours: Schedule backups during low-traffic periods
- Consistent Schedule: Use consistent backup times
- Daily Backups: Use daily backups for production databases
- Test Backups: Regularly verify backups are working
Retention Management
- Balance Retention: Balance retention with storage needs
- Compliance: Meet any regulatory retention requirements
- Recovery Needs: Set retention based on recovery needs
- Storage Monitoring: Monitor backup storage usage
Security
- Encryption: Backup encryption is automatic and always enabled
- Access Control: Control who can access backup settings
- Offsite Storage: Backups are automatically stored offsite
- Regular Testing: Test restore procedures regularly
Monitoring
- Backup Status: Regularly check backup status
- Storage Usage: Monitor backup storage usage
- Backup History: Review backup history regularly
- Failed Backups: Address failed backups immediately
Troubleshooting
Backups Not Running
If backups are not running:
- Check Settings: Verify backup settings are saved correctly
- Check Schedule: Verify backup time and frequency are correct
- Check Status: Verify backups are enabled
- Contact Support: Reach out to KloudBean support if issues persist
Backup Failures
If backups fail:
- Review Settings: Check backup settings for issues
- Check Storage: Verify sufficient storage is available
- Check Database: Verify database is accessible
- Contact Support: Contact KloudBean support for assistance
Storage Issues
If you have storage concerns:
- Review Retention: Adjust retention period if needed
- Check Frequency: Consider backup frequency impact on storage
- Monitor Usage: Monitor backup storage usage regularly
- Contact Support: Reach out to KloudBean support for storage options
Next Steps
After configuring backup settings:
- Learn about Restoring Database from Backup to restore your database
- Review Monitoring Database Server Health to track database performance
- Explore Controlling Database Access for access management