Launching Elasticsearch
Learn how to launch and deploy Elasticsearch on KloudBean. KloudBean provides managed Elasticsearch database with high performance and robust security policies.
Overview
KloudBean provides managed Elasticsearch database. KloudBean databases are high performant and having good security policies as well.
KloudBean Managed Elasticsearch Benefits
High Performance:
- Optimized Configuration: Pre-configured for optimal performance
- Fast Search: Distributed search and analytics engine for fast queries
- Efficient Resource Usage: Smart resource allocation
- Scalable Architecture: Built to scale horizontally with clusters
- Real-Time Search: Near real-time search capabilities
Security Policies:
- Encrypted Connections: SSL/TLS encryption for secure connections
- Access Control: Granular access control and IP whitelisting
- Authentication: Built-in authentication and authorization
- Regular Updates: Automatic security updates and patches
Easy Setup and Access:
- Few Steps Installation: It is a few steps installation process
- Quick Deployment: Database creation takes only 2-5 minutes
- Simple Configuration: Minimal configuration required
- Easy Access: Straightforward access to database credentials
- User-Friendly Interface: Intuitive dashboard for management
Additional Benefits:
- High Availability: Built-in cluster mode for redundancy
- Monitoring: Real-time performance monitoring
- Scalability: Easy scaling as your needs grow
- Support: Expert support from KloudBean team
- Full-Text Search: Advanced full-text search capabilities
Prerequisites
- An active KloudBean account
- Understanding of search and analytics requirements
- Payment method for database provisioning
Launching Elasticsearch Database
Step 1: Navigate to Database Section
In order to launch Elasticsearch database:
From your KloudBean dashboard navigate to Managed database or from top header click on "DBS".
On DBS page there is a button "Launch Database".
Once you click it will take you to database provision page.
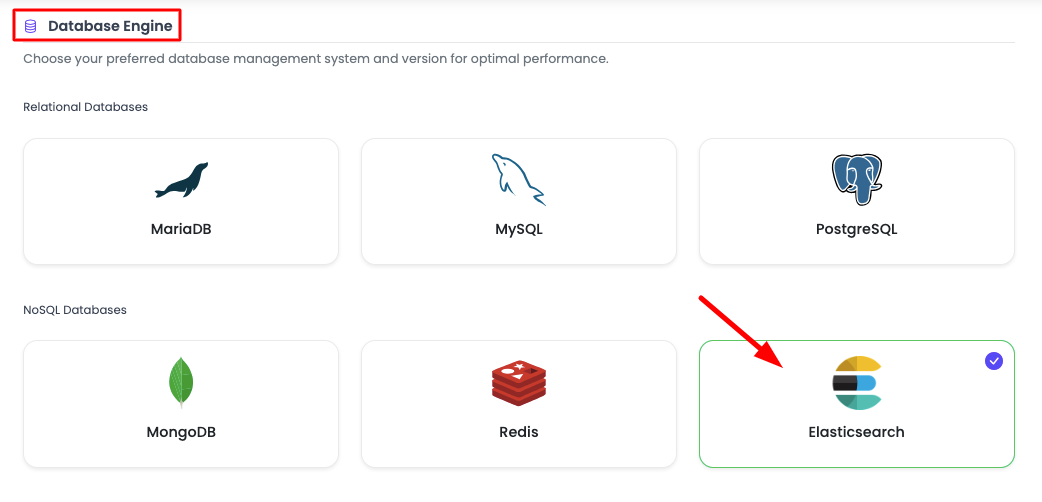
Step 2: Select Database Engine
Where you have to select:
Database engine: Select Elasticsearch from here.
Step 3: Provide Database Details
Next step is to provide following database detail:
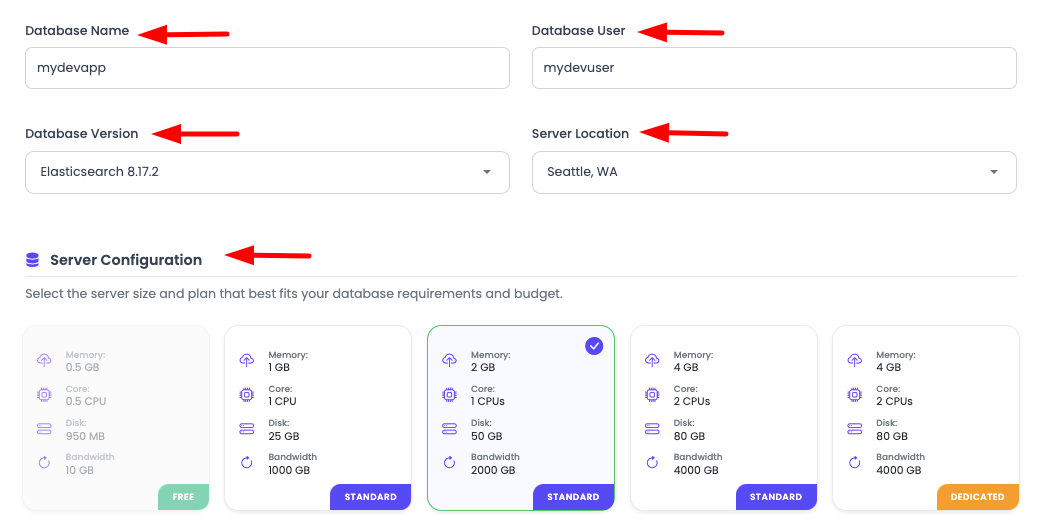
Required Information:
-
Database Name:
- Enter a unique name for your Elasticsearch cluster
- Use lowercase letters, numbers, and underscores
- Example:
myapp_search,analytics_cluster
-
Database User:
- Create a username for Elasticsearch access
- Use lowercase letters, numbers, and underscores
- Example:
elastic_user,search_admin
-
Database Version:
- Select Elasticsearch version:
- Elasticsearch 8.x (latest, recommended)
- Elasticsearch 7.x (stable)
- Choose based on your application requirements
- Select Elasticsearch version:
-
Server Location:
- Choose the geographic location for your database
- Select region closest to your application servers
- Consider data residency requirements
Step 4: Select Server Size
Once these details are added:
Decide server size and select most suitable size. Note that you can scale your database up any time, contact KloudBean for that.
Server Size Options:
- Small: Suitable for development and testing
- Medium: Good for small to medium applications
- Large: For production applications with high traffic
- Custom: Custom configuration for specific needs
Scaling Options:
- Vertical Scaling: Increase CPU, RAM, or storage
- Horizontal Scaling: Add nodes to cluster
- Contact Support: Reach out to KloudBean support for scaling assistance
Considerations:
- Current Needs: Start with size that meets current needs
- Growth Projection: Consider future growth when selecting size
- Cost Optimization: Start smaller and scale as needed
- Performance: Larger sizes offer better performance
- Memory Requirements: Elasticsearch requires sufficient RAM (minimum 2GB per node)
Step 5: Launch Database
Click on "Launch now" button, it will take you to the payment screen, where you will complete your payment.
Payment Process:
- Review Configuration: Verify all settings are correct
- Payment Method: Select your payment method
- Complete Payment: Complete the payment process
- Confirmation: Receive confirmation of payment
Once payment is completed, your database creation process will be initiated, and it will take around 2-5 minutes to create and configure your high performance database.
Creation Process:
- Database instance provisioning
- Elasticsearch installation and configuration
- Security setup and encryption
- Network configuration
Once created you will see your database in DBS page.
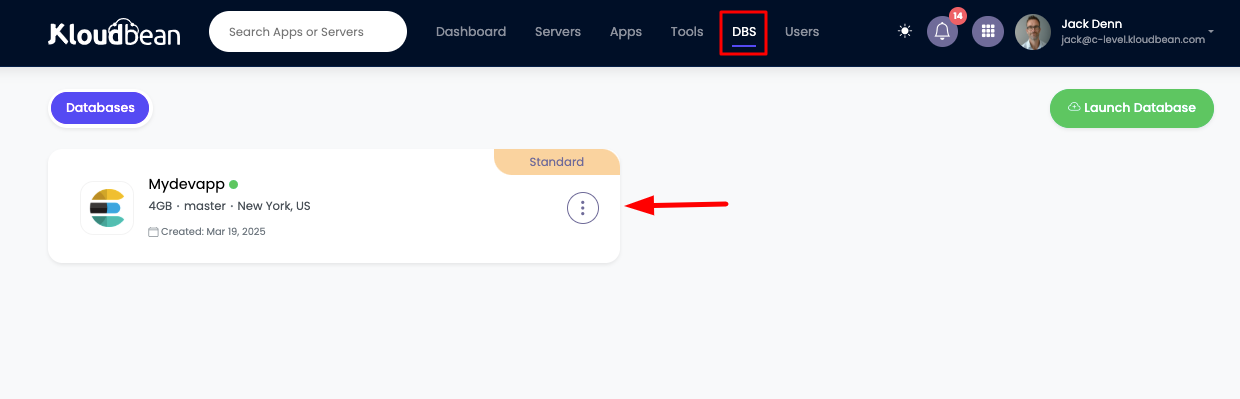
Accessing Database Details
Step 1: Navigate to Database Administration
In order to get database access detail click on your database and it will take you to database administration page where all the database access information is listed.
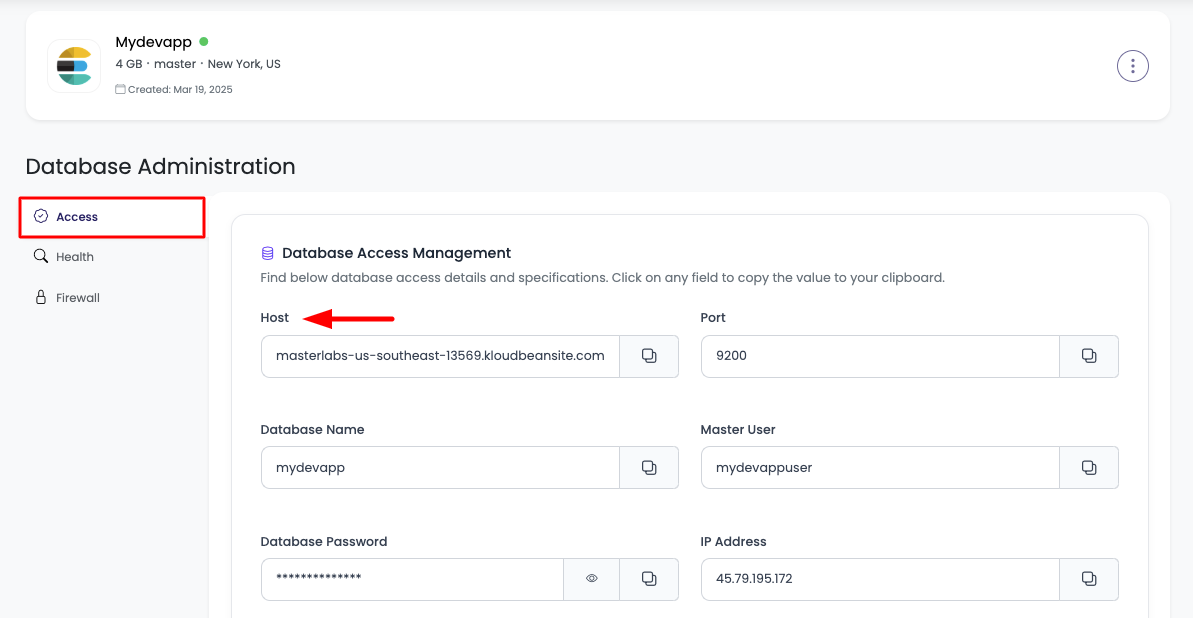
Step 2: View Database Credentials
Database Access Information:
Host:
- Database server hostname or IP address
- Use this to connect to your database
- Example:
elasticsearch-123456.kloudbeansite.comor192.168.1.100
Port:
- Elasticsearch port numbers:
- 9200: HTTP API port
- 9300: Transport port (internal cluster communication)
- Default Elasticsearch ports for connections
- Example:
9200for HTTP API
Database Name:
- Name of your Elasticsearch cluster
- Use this for identification
- Example:
myapp_search
Master User:
- Username for Elasticsearch access (usually "elastic")
- Primary database user credentials
- Example:
elastic,elastic_user
Database Password:
- Password for Elasticsearch authentication
- Keep this secure and never expose publicly
- Use this with Master User for authentication
IP Address:
- Database server IP address
- Use for IP whitelisting if needed
- Example:
192.168.1.100
You can use this information to use this database in your application.
Accessing Database
Database Access Status
By default, the public access to your database is disabled.
In order to check access status, navigate to "Database Specifications" section of "Access" tab.
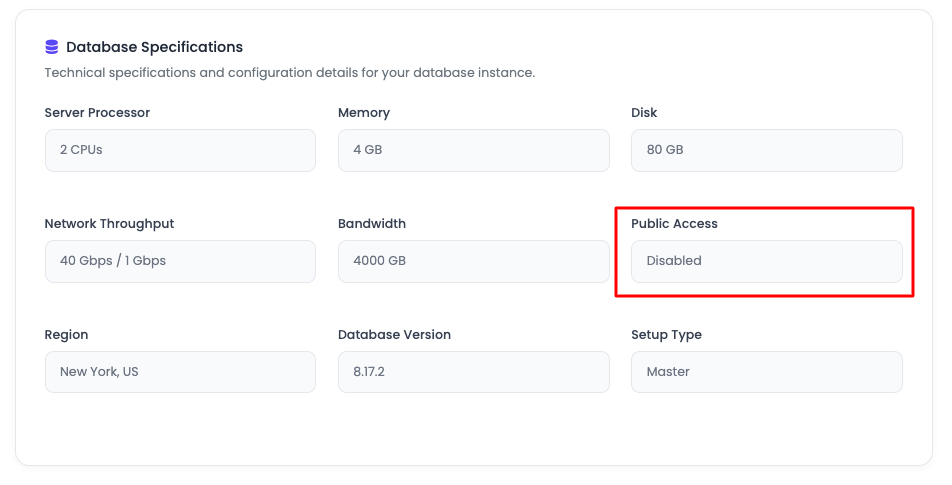
This represents that access is disabled and you cannot access it.
Enabling Database Access
In order to access database you have to whitelist the IP address of your source server or you have to enable public access of your database.
Important: Do Not Enable Public Access Unnecessarily
Why Public Access Should Be Avoided:
- Security Risk: Public access exposes your database to the entire internet
- Attack Surface: Increases vulnerability to attacks and unauthorized access
- Compliance Issues: May violate data protection regulations
- Best Practice: Always use IP whitelisting instead of public access
When Public Access Might Be Needed:
- Development/Testing: Only for non-production environments
- Temporary Access: For specific, time-limited tasks
- With Additional Security: Combined with strong passwords and SSL
Recommended Approach:
- IP Whitelisting: Always prefer IP whitelisting over public access
- Specific IPs: Whitelist only specific IP addresses that need access
- Source Server IP: Whitelist your application server's IP address
- VPN Access: Consider VPN for additional security layer
To get to know how you can update database access, read document: Controlling Database Access
Once access is enabled, now you can access your database.
Accessing Database from Shell/Command Line
Step 1: Install curl (for API Access)
On Linux (Ubuntu/Debian):
sudo apt update
sudo apt install curl
On macOS:
# curl is pre-installed
On Windows:
- Download curl from curl Downloads
- Or use PowerShell's Invoke-WebRequest
Step 2: Test Connection
Basic Connection Test:
curl -u [USERNAME]:[PASSWORD] https://[HOST]:[PORT]
Example:
curl -u elastic:your_password https://elasticsearch-123456.kloudbeansite.com:9200
You should receive a JSON response with cluster information.
Step 3: Basic Elasticsearch Commands
Cluster Health:
curl -u [USERNAME]:[PASSWORD] https://[HOST]:[PORT]/_cluster/health
Example:
curl -u elastic:your_password https://elasticsearch-123456.kloudbeansite.com:9200/_cluster/health
Cluster Info:
curl -u [USERNAME]:[PASSWORD] https://[HOST]:[PORT]/
Node Info:
curl -u [USERNAME]:[PASSWORD] https://[HOST]:[PORT]/_nodes
Create Index:
curl -X PUT -u [USERNAME]:[PASSWORD] https://[HOST]:[PORT]/[INDEX_NAME] \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-d '{
"settings": {
"number_of_shards": 1,
"number_of_replicas": 1
}
}'
Example:
curl -X PUT -u elastic:your_password https://elasticsearch-123456.kloudbeansite.com:9200/my_index \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-d '{
"settings": {
"number_of_shards": 1,
"number_of_replicas": 1
}
}'
Index Document:
curl -X POST -u [USERNAME]:[PASSWORD] https://[HOST]:[PORT]/[INDEX_NAME]/_doc \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-d '{
"field1": "value1",
"field2": "value2"
}'
Example:
curl -X POST -u elastic:your_password https://elasticsearch-123456.kloudbeansite.com:9200/my_index/_doc \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-d '{
"title": "Example Document",
"content": "This is the content",
"created_at": "2024-01-15T10:00:00Z"
}'
Get Document:
curl -u [USERNAME]:[PASSWORD] https://[HOST]:[PORT]/[INDEX_NAME]/_doc/[DOCUMENT_ID]
Search Documents:
curl -X GET -u [USERNAME]:[PASSWORD] "https://[HOST]:[PORT]/[INDEX_NAME]/_search?q=field:value"
Example:
curl -X GET -u elastic:your_password "https://elasticsearch-123456.kloudbeansite.com:9200/my_index/_search?q=title:example"
Advanced Search:
curl -X POST -u [USERNAME]:[PASSWORD] https://[HOST]:[PORT]/[INDEX_NAME]/_search \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-d '{
"query": {
"match": {
"field": "value"
}
}
}'
Delete Index:
curl -X DELETE -u [USERNAME]:[PASSWORD] https://[HOST]:[PORT]/[INDEX_NAME]
List All Indices:
curl -u [USERNAME]:[PASSWORD] https://[HOST]:[PORT]/_cat/indices?v
Get Index Mapping:
curl -u [USERNAME]:[PASSWORD] https://[HOST]:[PORT]/[INDEX_NAME]/_mapping
Using Database Credentials in Your Application
Connection String Format
Standard Elasticsearch Connection String:
https://[USERNAME]:[PASSWORD]@[HOST]:[PORT]
Example:
https://elastic:[email protected]:9200
Node.js
Using @elastic/elasticsearch package:
const { Client } = require('@elastic/elasticsearch');
const client = new Client({
node: 'https://elasticsearch-123456.kloudbeansite.com:9200',
auth: {
username: 'elastic',
password: 'your_password'
}
});
// Test connection
async function testConnection() {
const health = await client.cluster.health();
console.log(health);
}
// Index document
async function indexDocument() {
await client.index({
index: 'my_index',
document: {
title: 'Example Document',
content: 'This is the content',
created_at: new Date()
}
});
}
// Search documents
async function searchDocuments() {
const result = await client.search({
index: 'my_index',
query: {
match: {
title: 'example'
}
}
});
console.log(result.hits.hits);
}
testConnection();
Python
Using elasticsearch package:
from elasticsearch import Elasticsearch
es = Elasticsearch(
['https://elasticsearch-123456.kloudbeansite.com:9200'],
http_auth=('elastic', 'your_password')
)
# Test connection
health = es.cluster.health()
print(health)
# Index document
es.index(
index='my_index',
document={
'title': 'Example Document',
'content': 'This is the content',
'created_at': '2024-01-15T10:00:00Z'
}
)
# Search documents
result = es.search(
index='my_index',
query={
'match': {
'title': 'example'
}
}
)
print(result['hits']['hits'])
PHP
Using elasticsearch/elasticsearch package:
<?php
require 'vendor/autoload.php';
use Elasticsearch\ClientBuilder;
$client = ClientBuilder::create()
->setHosts(['https://elastic:[email protected]:9200'])
->build();
// Test connection
$health = $client->cluster()->health();
print_r($health);
// Index document
$params = [
'index' => 'my_index',
'body' => [
'title' => 'Example Document',
'content' => 'This is the content',
'created_at' => date('c')
]
];
$response = $client->index($params);
// Search documents
$params = [
'index' => 'my_index',
'body' => [
'query' => [
'match' => [
'title' => 'example'
]
]
]
];
$response = $client->search($params);
print_r($response['hits']['hits']);
?>
Best Practices
Security
- Strong Passwords: Use strong, unique passwords for Elasticsearch
- IP Whitelisting: Always use IP whitelisting instead of public access
- SSL/TLS: Enable SSL/TLS encryption for all connections
- Regular Updates: Keep Elasticsearch updated to latest version
- Access Control: Implement proper user permissions and access control
Performance
- Proper Indexing: Create appropriate indexes and mappings
- Query Optimization: Optimize your search queries
- Shard Configuration: Configure appropriate number of shards
- Resource Monitoring: Monitor cluster health and performance regularly
- Regular Maintenance: Perform regular index optimization
- Memory Management: Ensure sufficient heap memory allocation
Management
- Monitor Usage: Monitor cluster health and performance
- Scale When Needed: Scale your cluster as your needs grow
- Documentation: Document your index mappings and configurations
- Version Control: Keep track of index changes
Troubleshooting
Connection Issues
Cannot Connect to Database:
- Check IP Whitelist: Verify your IP is whitelisted
- Check Credentials: Verify host, port, username, and password
- Check Network: Verify network connectivity
- Check Firewall: Check firewall rules
- Review Access Settings: Check database access configuration
- Check SSL: Verify SSL/TLS configuration
Authentication Errors:
- Verify Credentials: Check username and password
- Check User Permissions: Verify user has necessary permissions
- Check Configuration: Verify Elasticsearch security configuration
Performance Issues
Slow Queries:
- Check Indexes: Verify proper indexes and mappings exist
- Optimize Queries: Review and optimize slow queries
- Check Resources: Monitor CPU, memory, and disk usage
- Review Configuration: Review Elasticsearch configuration
- Check Shard Allocation: Verify shard allocation is optimal
Cluster Health Issues:
- Check Cluster Status: Monitor cluster health status
- Check Node Status: Verify all nodes are healthy
- Check Disk Space: Monitor disk usage
- Review Logs: Check Elasticsearch logs for errors
Memory Issues:
- Check Heap Size: Verify heap memory allocation
- Monitor Memory: Check memory usage with cluster stats
- Increase Resources: Consider increasing server size
Next Steps
After launching your Elasticsearch database:
- Learn about Controlling Database Access for managing access
- Review Monitoring Database Server Health for monitoring
- Check Launching Redis for caching solutions